Antihistamines are medications that block the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body in response to allergic reactions and inflammation. They can be classified into different types based on their receptor selectivity and generation. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Types: H1 and H2 Receptor antihistamines
Generation: 1st and 2nd generation
Types of Antihistamines:
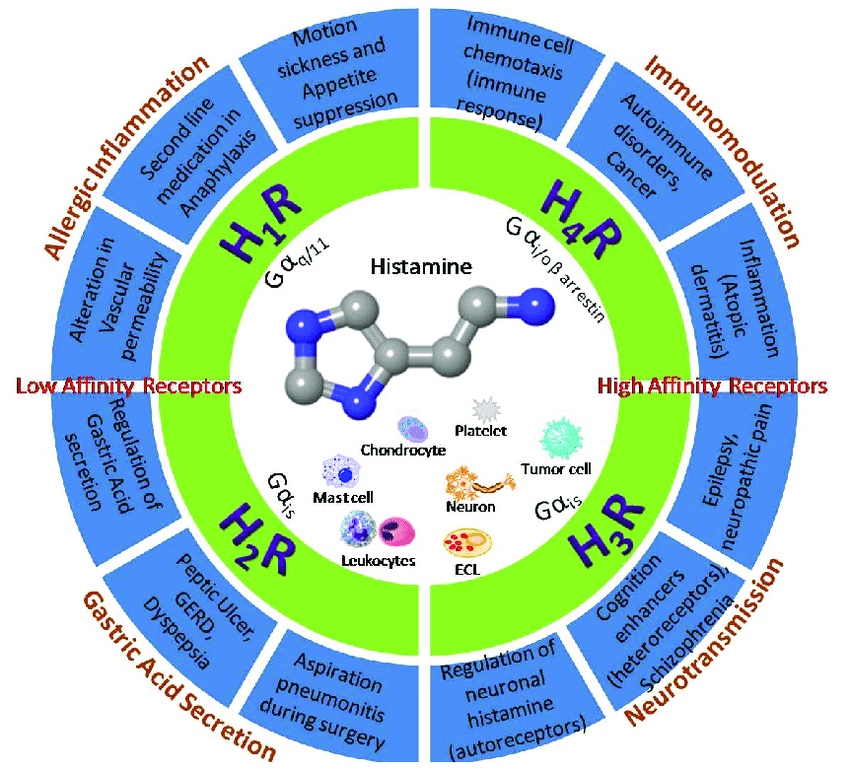
1. H1 Receptor Antihistamines:
– These antihistamines primarily target the H1 histamine receptors, which are found on various cells in the body, including those in the respiratory tract, blood vessels, and skin.
– They are used to treat allergic reactions, such as sneezing, itching, runny nose, and watery eyes.
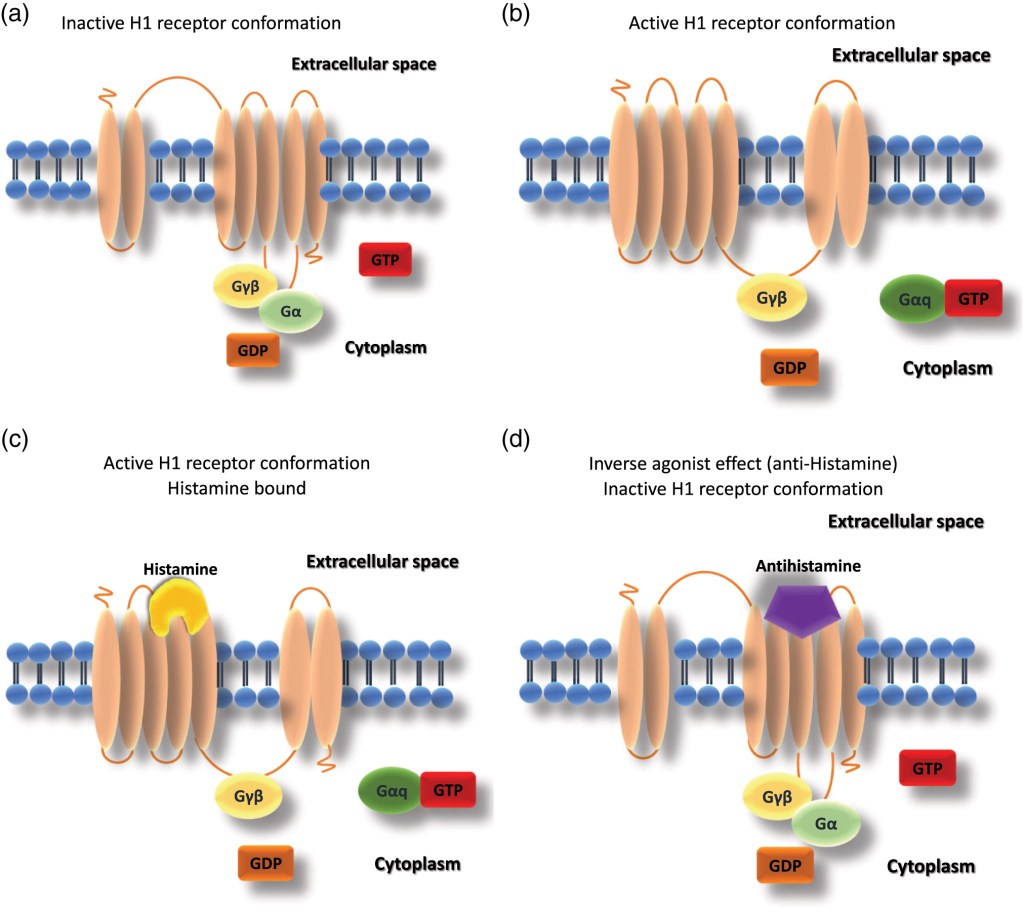
2. H2 Receptor Antihistamines:
– These antihistamines target the H2 histamine receptors, which are mainly found in the stomach lining. They play a role in regulating stomach acid production.
– They are primarily used to reduce stomach acid and treat conditions like gastric ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Examples of Antihistamines:

1. First-Generation H1 Antihistamines (Sedating):
– Examples: Diphenhydramine, Chlorpheniramine, Clemastine, Promethazine.
– These antihistamines can cause drowsiness due to their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and affect the central nervous system.
– They are effective in treating allergy symptoms but can impair alertness and concentration.


2. Second-Generation H1 Antihistamines (Non-Sedating):
– Examples: Loratadine, Cetirizine, Fexofenadine, Desloratadine.
– These antihistamines have reduced or no sedative effects because they have limited ability to cross the blood-brain barrier.
– They are preferred for daytime use and situations where sedation is undesirable.
For the dose of each antihistamine, you can visit https://www.drugs.com/dosage/
In summary, antihistamines are categorized based on their receptor selectivity and generation. First-generation antihistamines can cause drowsiness due to their ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, while second-generation antihistamines have reduced sedative effects. They target H1 and H2 histamine receptors to treat different symptoms and conditions. Always consult a healthcare professional before using antihistamines to determine the most suitable option for your specific needs.






























Leave a comment