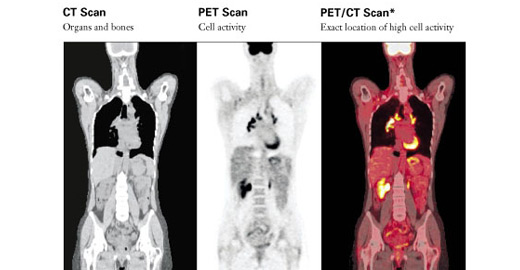
When it comes to the diagnosis and management of head and neck malignancies, accurate imaging plays a crucial role. Among the various imaging modalities available, positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) has emerged as a valuable tool in providing a window into the tumor.
This article aims to explore the significance of PET-CT scan in head and neck malignancy, its applications, the benefits it offers in the care of patients with these conditions, and the role of standardized uptake value (SUV) measurement, including SUV values for malignancy assessment.
Understanding PET-CT Scan
PET-CT combines the functional information obtained from positron emission tomography (PET) with the anatomical details provided by computed tomography (CT). PET utilizes a radioactive tracer, typically fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), which is taken up by metabolically active cells, such as cancer cells. By detecting the concentration of FDG, PET can highlight areas of increased metabolic activity, indicating the presence of tumors or areas with potential malignancy. The addition of CT imaging allows for precise anatomical localization of these areas, providing a comprehensive view of the tumor and its surrounding structures.
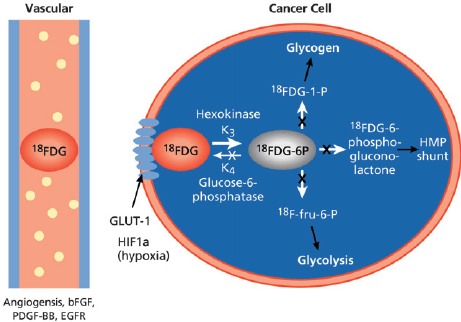
Standardized Uptake Value (SUV) Measurement
In PET imaging, the standardized uptake value (SUV) is a quantitative measure used to assess the level of FDG uptake within a tumor or lesion. SUV measurement provides valuable information about the metabolic activity of the tumor and helps in characterizing its aggressiveness. Higher SUV values often indicate a higher metabolic rate and increased tumor activity. The SUV measurement serves as an important parameter in cancer assessment and can assist in several aspects, including staging, treatment response evaluation, and predicting patient outcomes.
In head and neck malignancy, SUV values play a significant role in determining the extent and behavior of the tumor. Different malignancies can exhibit varying SUV values depending on their characteristics. For example, a higher SUV value in a head and neck tumor may suggest a more aggressive tumor phenotype and a higher likelihood of metastasis. On the other hand, a lower SUV value may indicate a less metabolically active tumor with a potentially better prognosis.
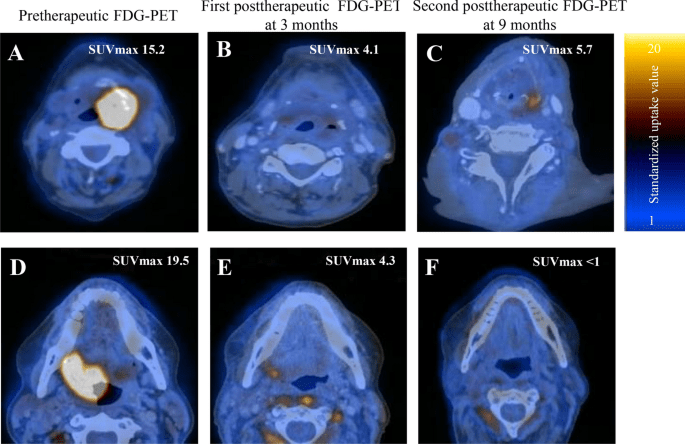
The specific SUV values for malignancy vary depending on the type of tumor, its location, and individual patient factors. Generally, SUV values above a certain threshold, such as 2.5 or 3.0, are considered indicative of malignancy. However, it is important to interpret SUV values in conjunction with other clinical and imaging findings for a comprehensive assessment.
Applications of PET-CT in Head and Neck Malignancy
1. Staging: PET-CT scan is highly valuable in the initial staging of head and neck malignancies. It provides detailed information about the primary tumor, lymph node involvement, and the presence of distant metastases. By accurately determining the extent of disease, including SUV measurements, PET-CT scan aids in treatment planning and prognostication.
2. Detection of Occult Primary Tumors: In some cases, patients may present with cervical lymphadenopathy without an identifiable primary tumor. PET-CT scan, along with SUV measurement, can help locate the occult primary tumor by detecting areas of increased metabolic activity, potentially guiding targeted biopsies and treatment decisions.
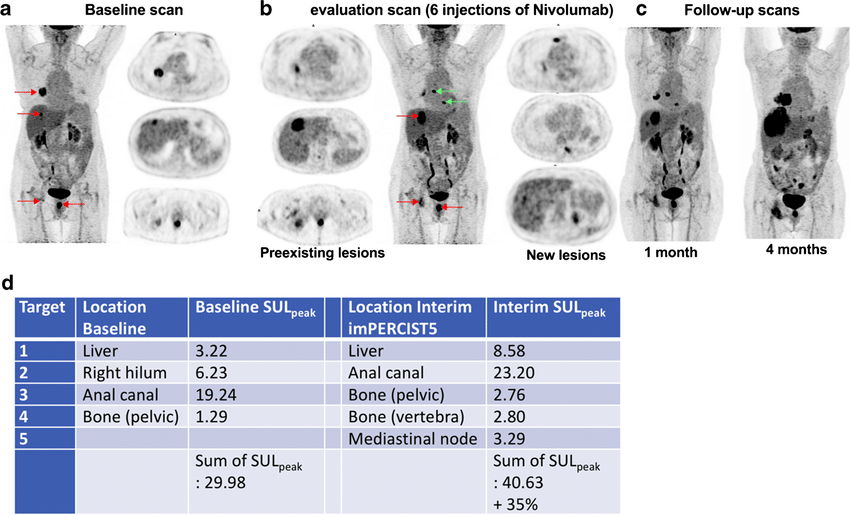
3. Assessment of Treatment Response: Following treatment, PET-CT scan, along with SUV measurement, can assess the response to therapy by comparing pre- and post-treatment images. It helps determine the effectiveness of treatment and aids in decision-making regarding further management, such as the need for additional surgery or adjuvant therapy.
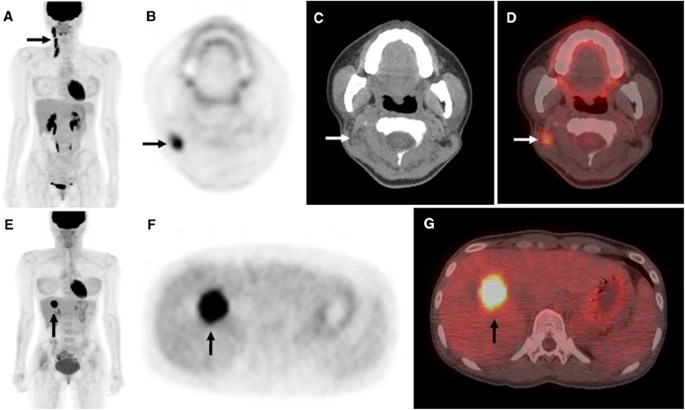
4. Detection of Recurrence: PET-CT scan, with SUV measurement, is instrumental in detecting recurrent disease in patients previously treated for head and neck malignancy. It can identify areas of increased metabolic activity, indicated by higher SUV values, that may indicate tumor recurrence, guiding further investigation and appropriate management.
Benefits of PET-CT Scan in Head and Neck Malignancy
1. Improved Accuracy: PET-CT scan, along with SUV measurement, provides a comprehensive evaluation by combining functional and anatomical information. This improves the accuracy of tumor detection, staging, treatment response assessment, and prediction of patient outcomes.

2. Precise Treatment Planning: By accurately identifying the extent of the tumor and its metabolic activity through SUV measurement, PET-CT scan aids in precise treatment planning. It allows for individualized treatment approaches, including surgical interventions, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies, based on the specific characteristics of the tumor.
3. Reduced Unnecessary Procedures: PET-CT scan, with its ability to accurately detect tumor involvement in lymph nodes and distant sites, helps in avoiding unnecessary procedures such as neck dissections. This reduces the risk of associated complications and improves patient outcomes.
4. Early Detection of Recurrence: With its high sensitivity in detecting recurrent disease, PET-CT scan, along with SUV measurement, enables early detection of tumor recurrence. Early intervention can lead to timely treatment and improved prognosis.

Are there any risks associated with PET-CT scan?
PET-CT scan involves exposure to a small amount of radiation from the radioactive tracer. However, the benefits of the scan usually outweigh the risks. The procedure is generally safe when performed by experienced healthcare professionals.

Origins of Radiation in PET/CT Imaging
Radiation in PET/CT scans emanates from two distinct sources. The primary source is internal, stemming from the injection of 18F-FDG, a positron-emitting substance that generates high-energy radiation during a PET scan. The secondary source is external, occurring when the patient subsequently undergoes a CT scan.

Conclusion
PET-CT scan, with its incorporation of SUV measurement, plays a significant role in the diagnosis and management of head and neck malignancy. It provides valuable information about tumor metabolism, aiding in staging, treatment response assessment, and detection of recurrence. The use of SUV values further enhances its accuracy and helps in characterizing the aggressiveness of the tumor. With its ability to guide precise treatment planning and reduce unnecessary procedures, PET-CT scan has become an indispensable tool in the care of patients with head and neck malignancy.






























Leave a comment