Introduction
Head and neck cancer is a complex disease that can have a significant impact on an individual’s health and quality of life. Detecting the early signs of this condition is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. In this article, we will explore the unheard whispers of head and neck cancer, uncovering its early warning signs and providing insights on how to manage it.
Understanding Head and Neck Cancer
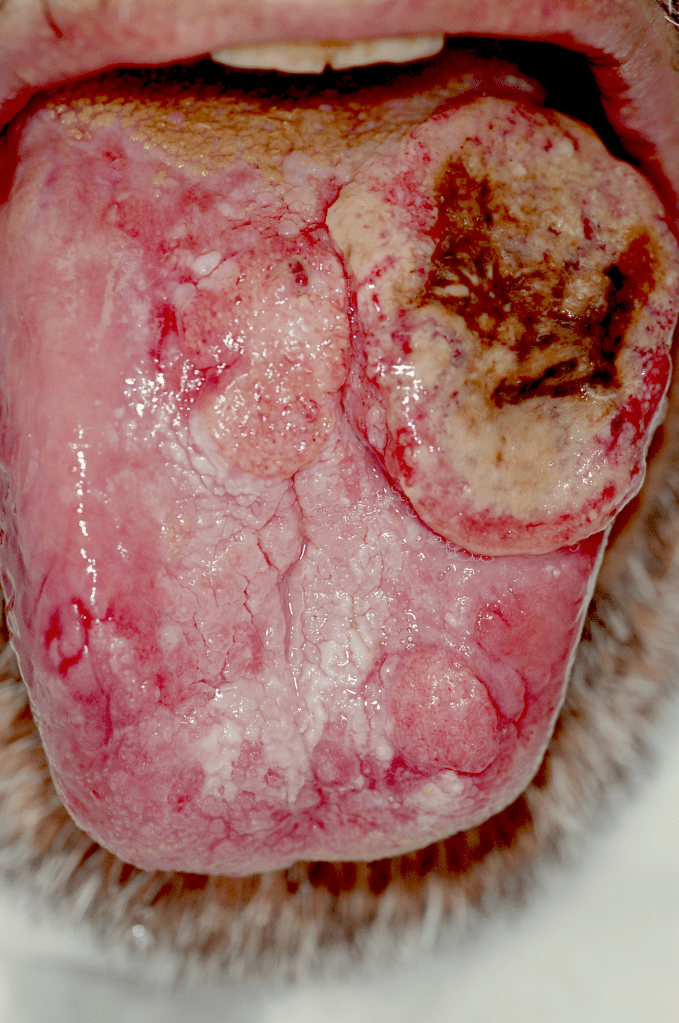
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that develop in the tissues of the head and neck region. This includes the oral cavity, throat (oropharynx), voice box (larynx), sinuses, and nasal passages. These cancers can arise from various cell types, such as squamous cells, salivary gland cells, or lymphatic tissue. Understanding the different types and locations of head and neck cancer is essential for early detection.
Common Risk Factors
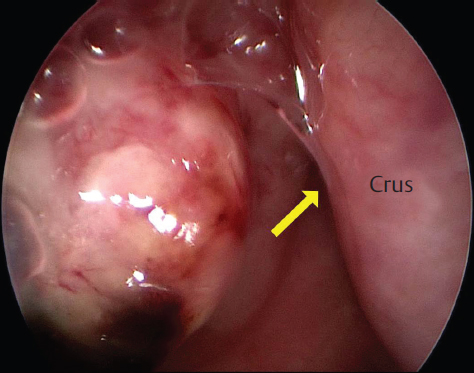
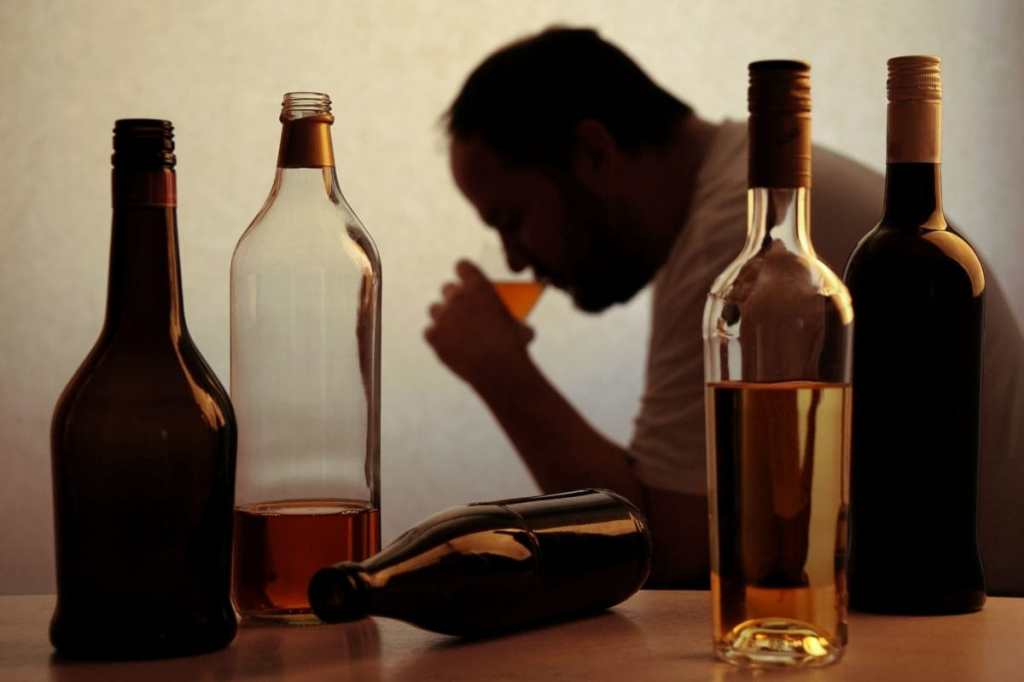
Several factors can increase the risk of developing head and neck cancer. These include tobacco and alcohol use, prolonged exposure to the sun, certain viral infections (such as Human PapillomaVirus or Epstein-Barr Virus), a weakened immune system, and a family history of the disease. It is crucial to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate measures to minimize the chances of developing head and neck cancer.




Recognizing the Early Signs
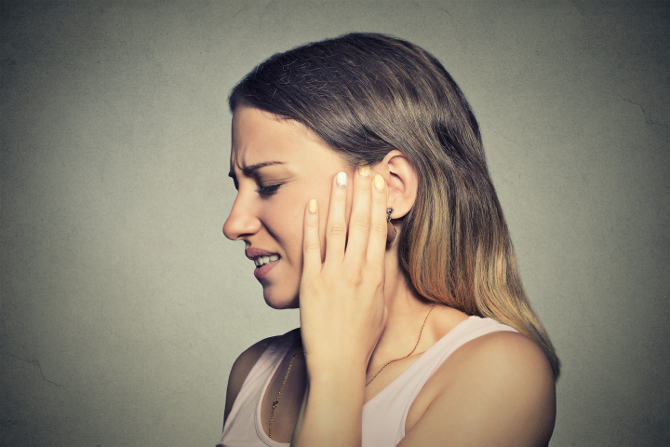
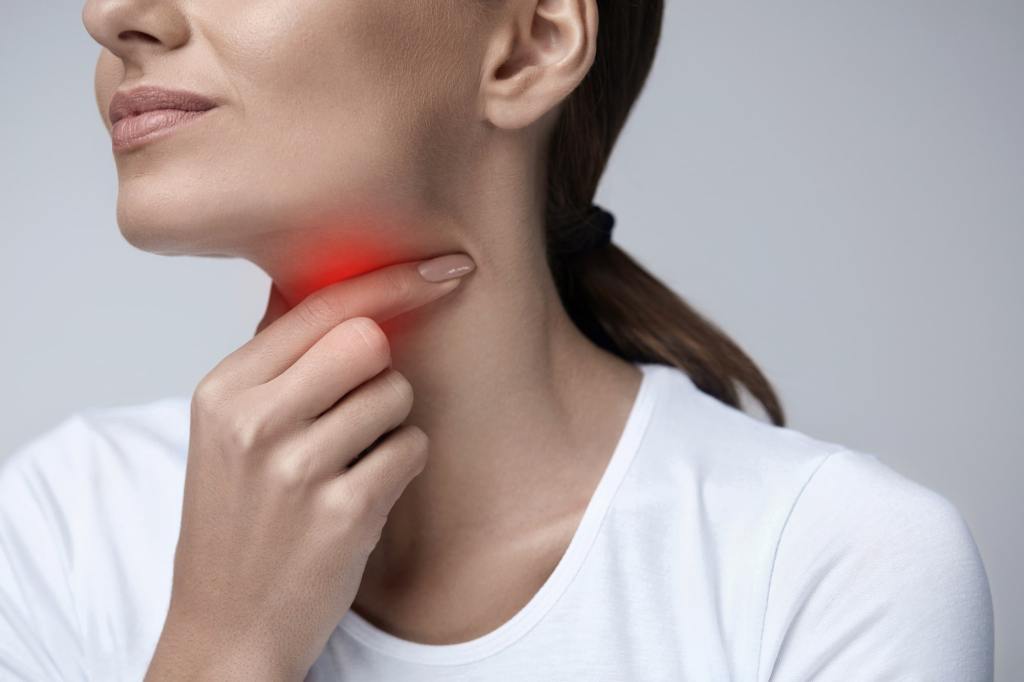
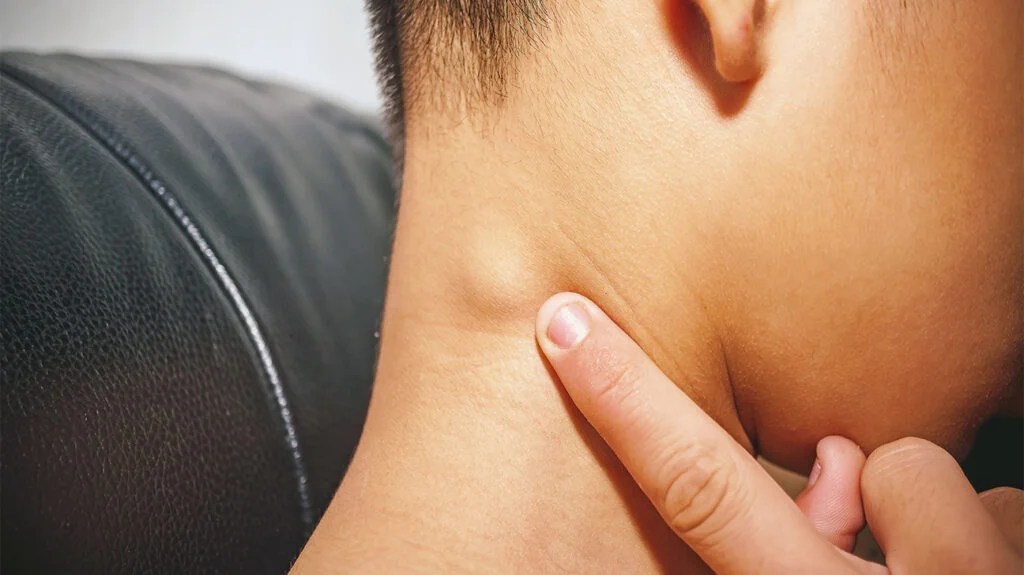
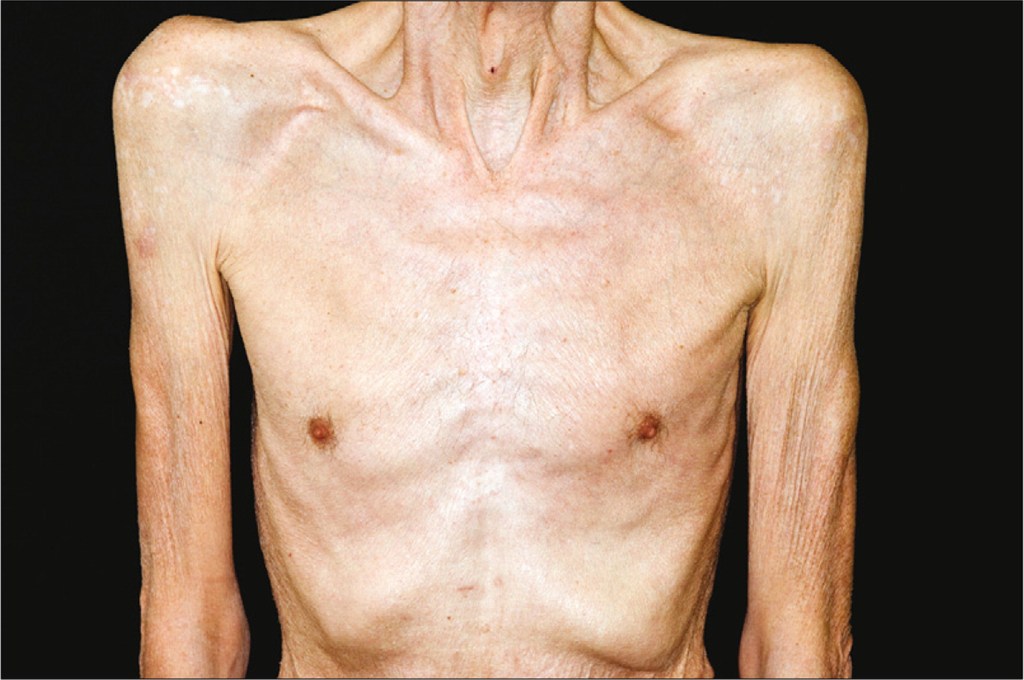
Early detection of head and neck cancer greatly improves the chances of successful treatment and recovery. It is vital to recognize the early warning signs, which may include persistent sore throat (odynophagia), difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), changes in voice or hoarseness, a lump or swelling in the neck, persistent earache (referred pain), unexplained weight loss, and chronic sinus infections. Paying attention to these symptoms and seeking medical evaluation is crucial.


Diagnostic Procedures
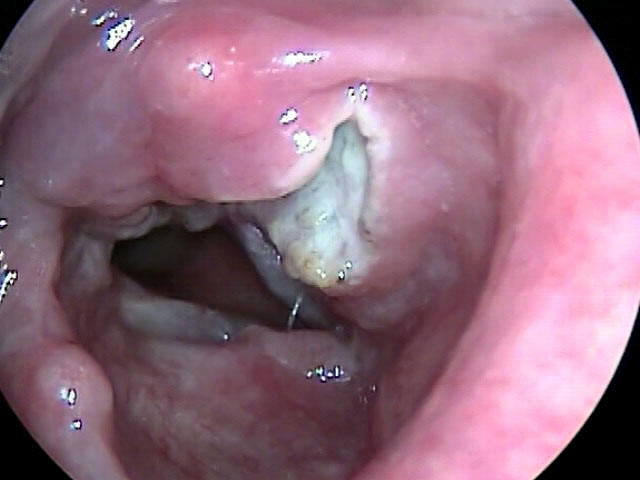
When symptoms or suspicious findings are present, healthcare professionals may recommend diagnostic procedures to confirm or rule out head and neck cancer. These procedures may include physical examinations, imaging tests like CT, MRI or PET scan, endoscopies, biopsies, and laboratory tests. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan.

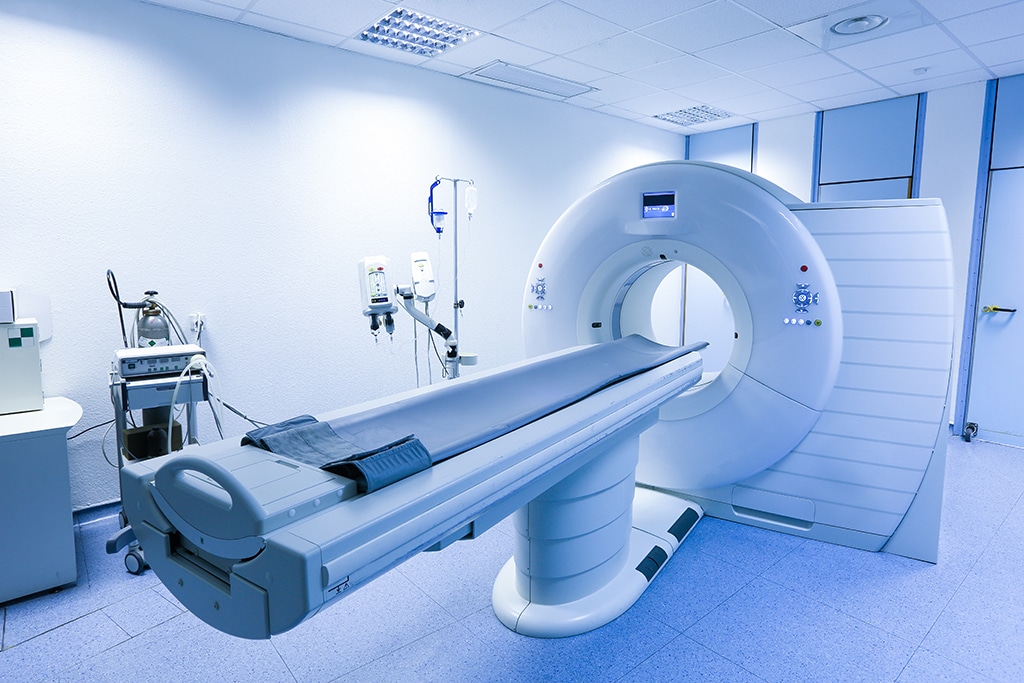
Treatment Options
Treatment for head and neck cancer depends on various factors, such as the type and stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. Common treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. A multidisciplinary approach involving specialists from different fields ensures comprehensive and personalized care
1. Surgery: Surgery is a common treatment for head and neck cancer and involves the removal of the tumor and nearby affected tissues. The extent of surgery depends on the size, location, and stage of the cancer. On occasion, the restoration of both functionality and aesthetic aspects may require the implementation of reconstructive surgery.

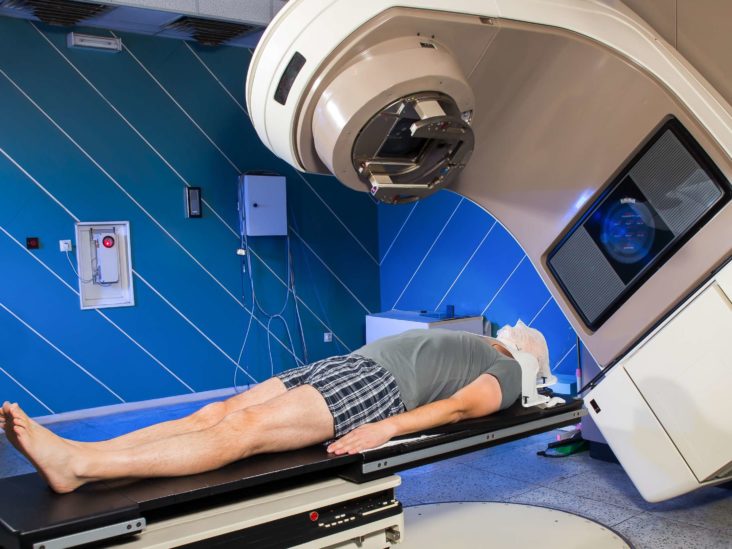
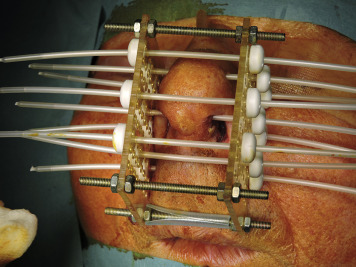
2. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other forms of radiation to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. It can be delivered externally (external beam radiation) or internally (brachytherapy) using radioactive materials. The employment of radiation therapy can be either singularly employed or employed in conjunction with alternative treatments.
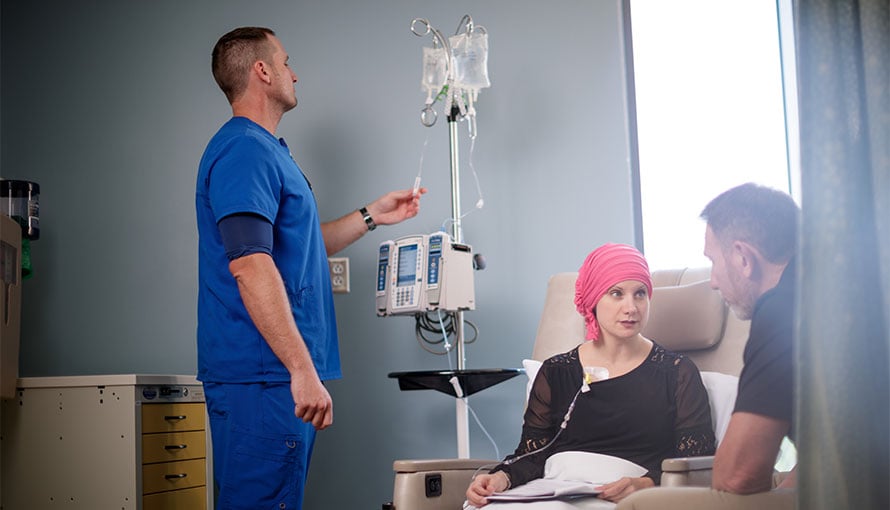
3. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapeutic treatment encompasses the administration of medications aimed at eliminating cancerous cells, frequently in conjunction with other therapeutic modalities like surgery or radiation therapy. Chemotherapy can be administered orally or intravenously and is usually given in cycles to allow the body time to recover between treatments.
4. Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target certain molecules or proteins involved in cancer growth and survival. These drugs interfere with specific pathways in cancer cells, inhibiting their growth and spread. Targeted therapy is often used in cases where specific genetic mutations or biomarkers are present in the tumor.
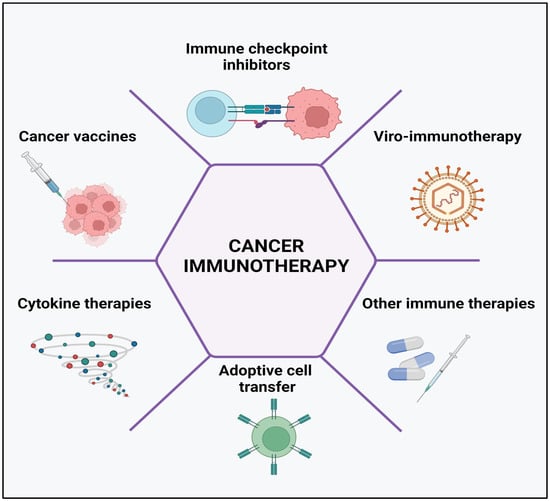
5. Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It involves the use of drugs that stimulate the immune system or enhance its ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Immunotherapy can help boost the immune response against head and neck cancer and has shown promising results in certain cases.
6. Palliative Care: Palliative care focuses on providing relief from symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients with advanced head and neck cancer. It involves a multidisciplinary approach that addresses physical, emotional, and psychological needs. Palliative care can be integrated with curative treatments or used as the main approach for patients with advanced or metastatic cancer.

It’s important to note that the choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the stage and location of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and individual preferences. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including surgeons, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, and other specialists, will work together to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each patient.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Although not all cases of head and neck cancer can be prevented, certain lifestyle modifications can reduce the risk. These include avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, practicing safe sun exposure, maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, protecting against HPV through vaccination, and practicing good oral hygiene. These simple yet impactful changes can contribute to overall well-being and lower the risk of developing cancer.


Support and Care for Patients
Receiving a diagnosis of head and neck cancer can be overwhelming for both patients and their loved ones. Establishing a robust support network is of utmost importance. Support groups, counseling services, and healthcare professionals specialized in cancer care can provide emotional support, information, and practical assistance throughout the treatment journey.

Coping with the Emotional Impact
The emotional impact of head and neck cancer extends beyond the physical symptoms. Coping with the diagnosis, treatment-related challenges, and potential changes in appearance and function can be challenging. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, seeking professional counseling, and connecting with others who have faced similar experiences can help individuals navigate the emotional aspects of living with head and neck cancer.

Conclusion
Detecting head and neck cancer in its early stages is crucial for successful treatment outcomes. By understanding the early signs and risk factors associated with this type of cancer, individuals can take proactive steps towards prevention, timely diagnosis, and effective management. Remember, if you experience any persistent symptoms or concerns, consult with a healthcare professional promptly. Shed light on the whispers of head and neck cancer, and take control of your health.






























Leave a comment