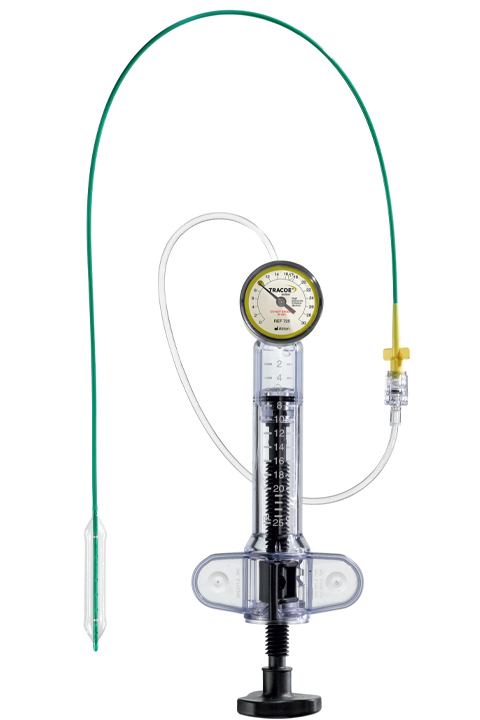
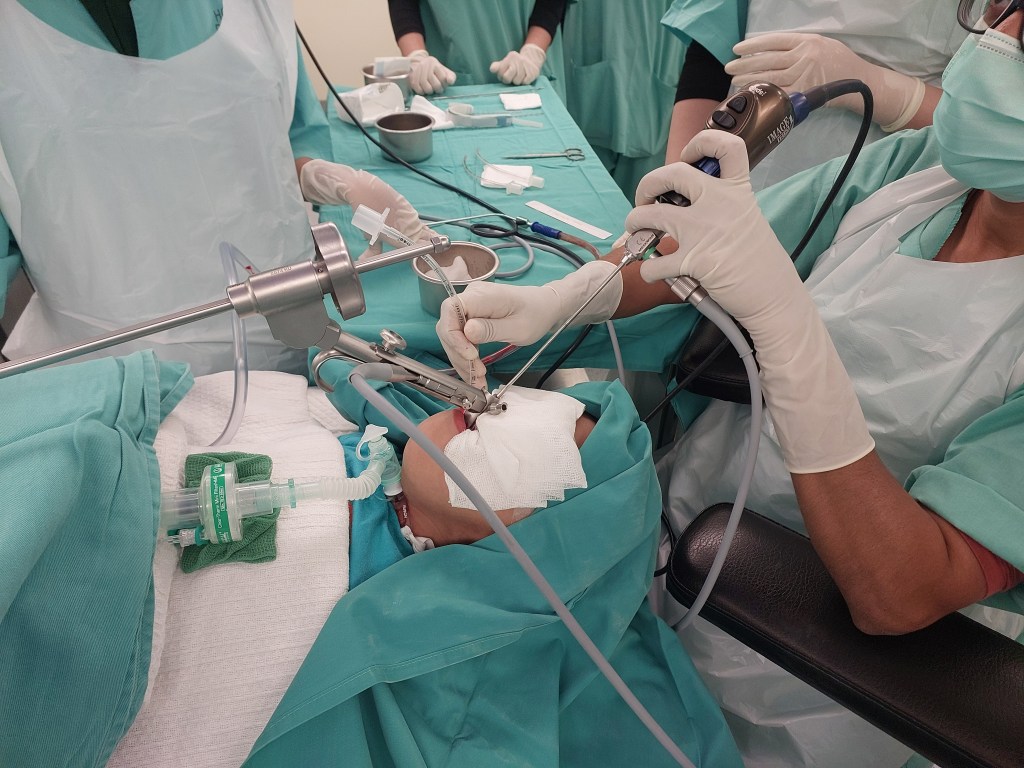
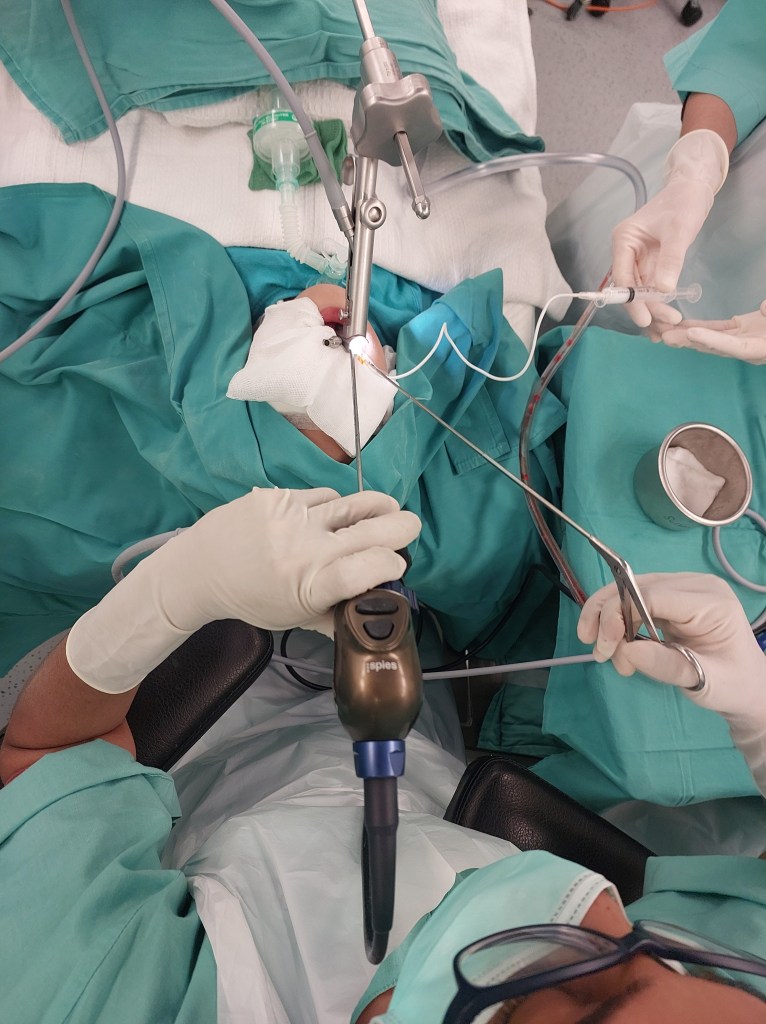
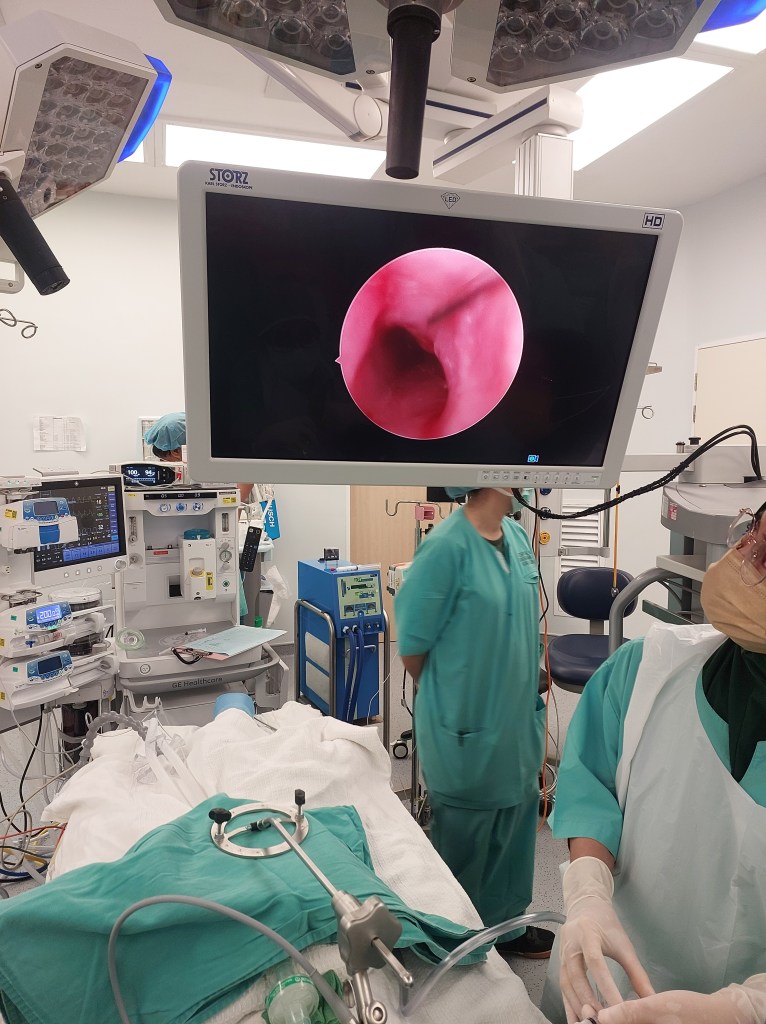
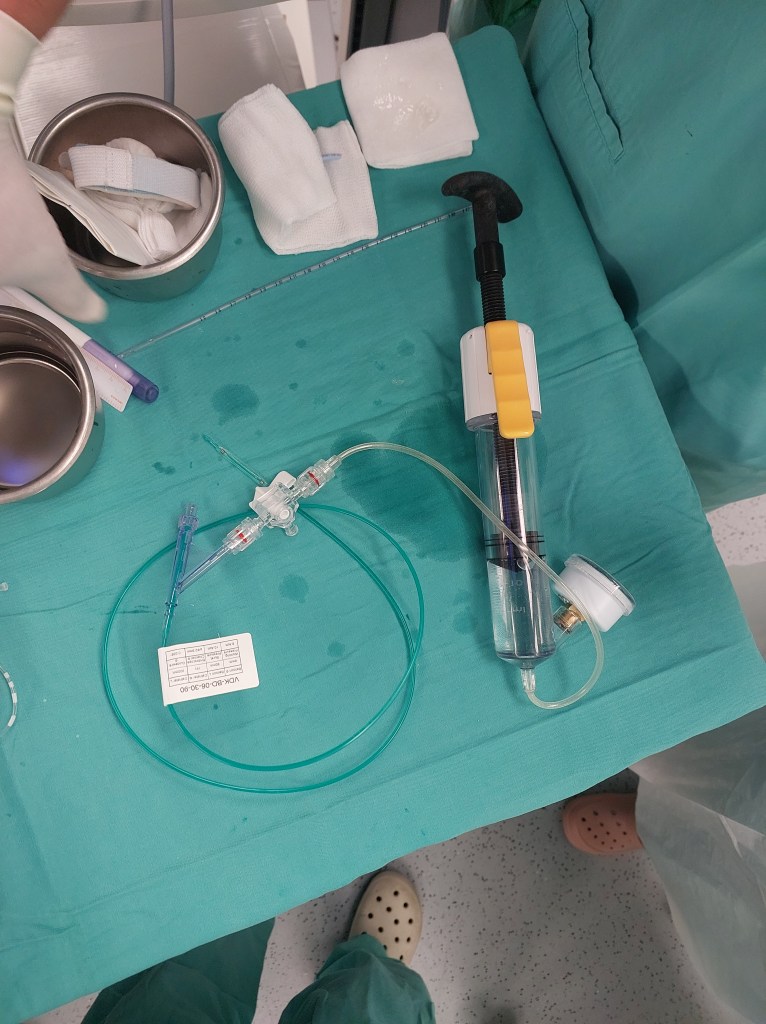
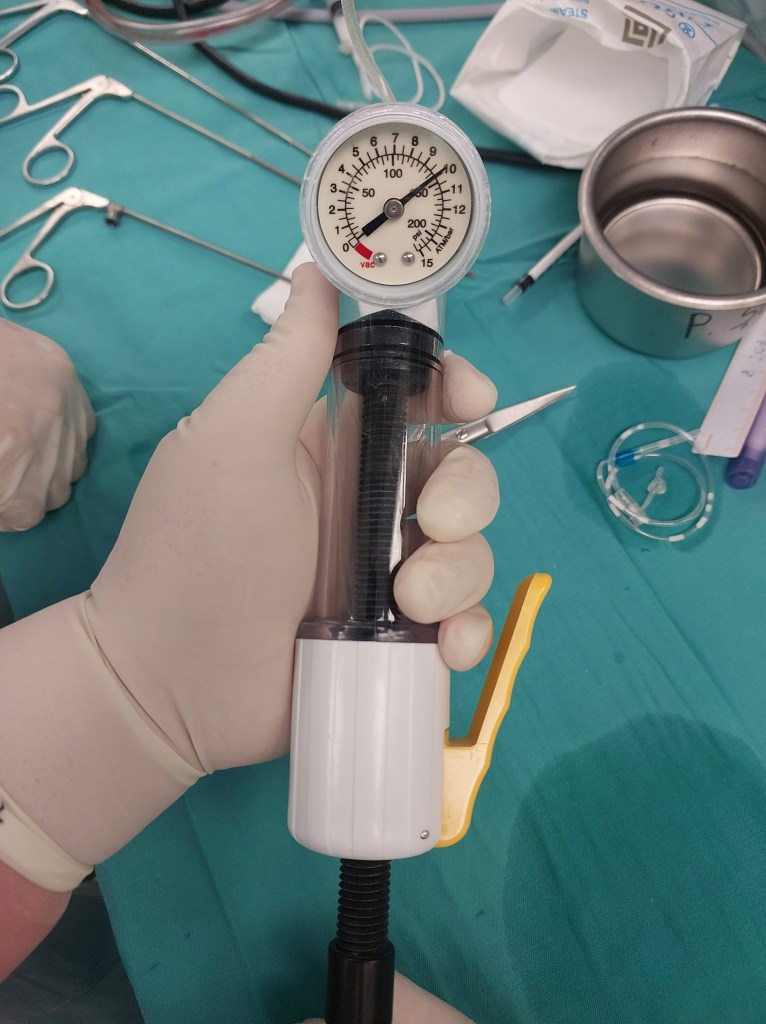
Balloon dilation (BD) was first introduced as a treatment option in 1984 for tracheal and bronchial stenoses. This procedure is suitable when the cartilaginous framework of the airway remains intact. Utilizing direct endoscopic guidance, a balloon is employed to exert radial pressure on the narrowed airway, aiming to minimize the likelihood of mucosal damage and subsequent restenosis.
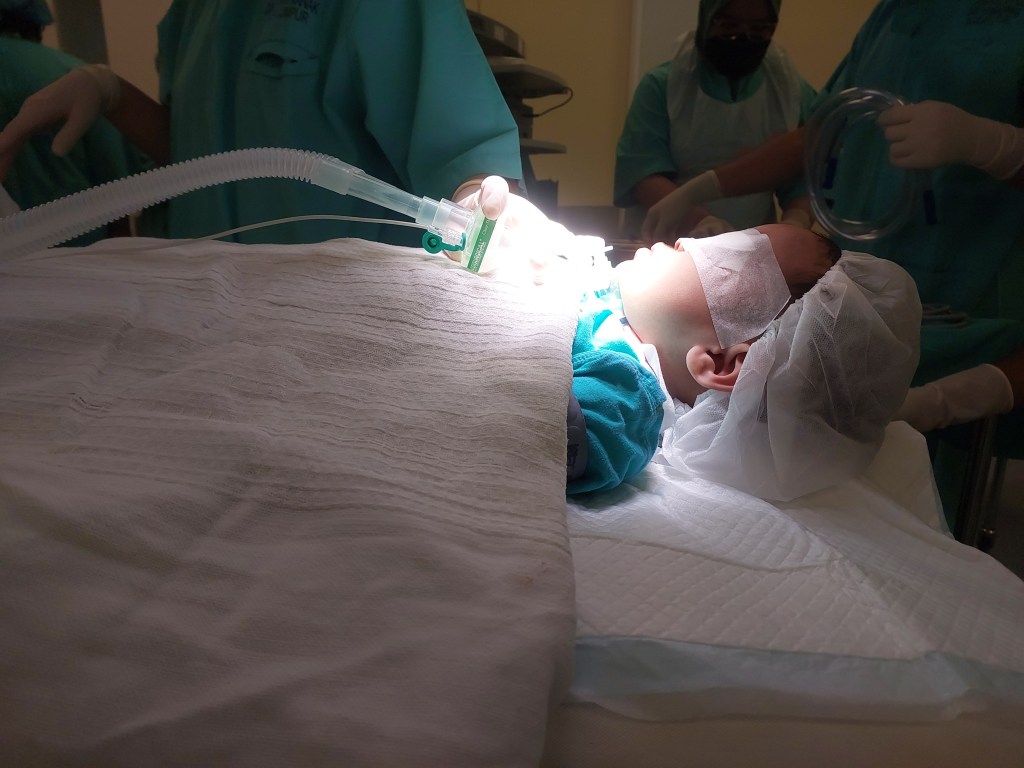
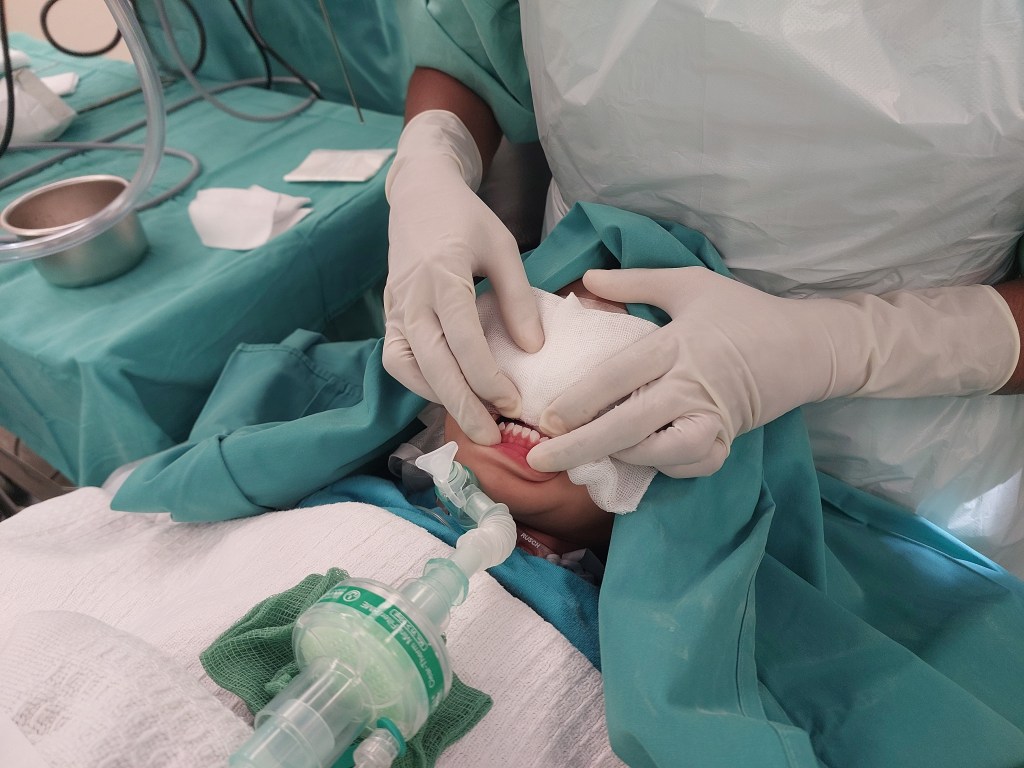
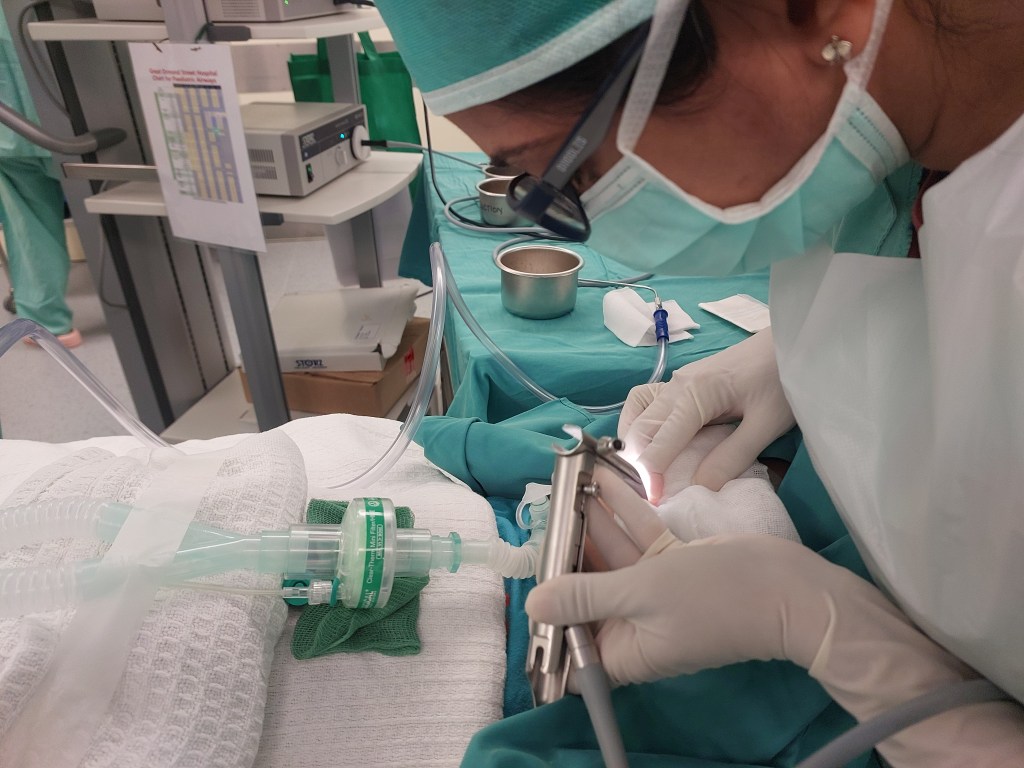
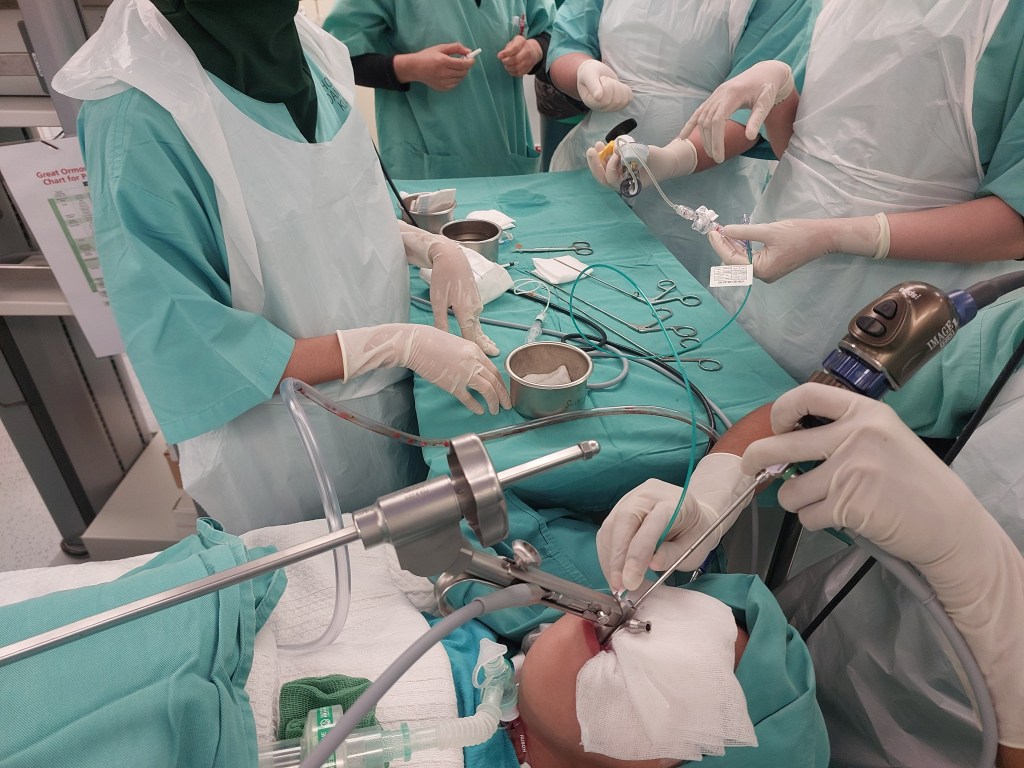
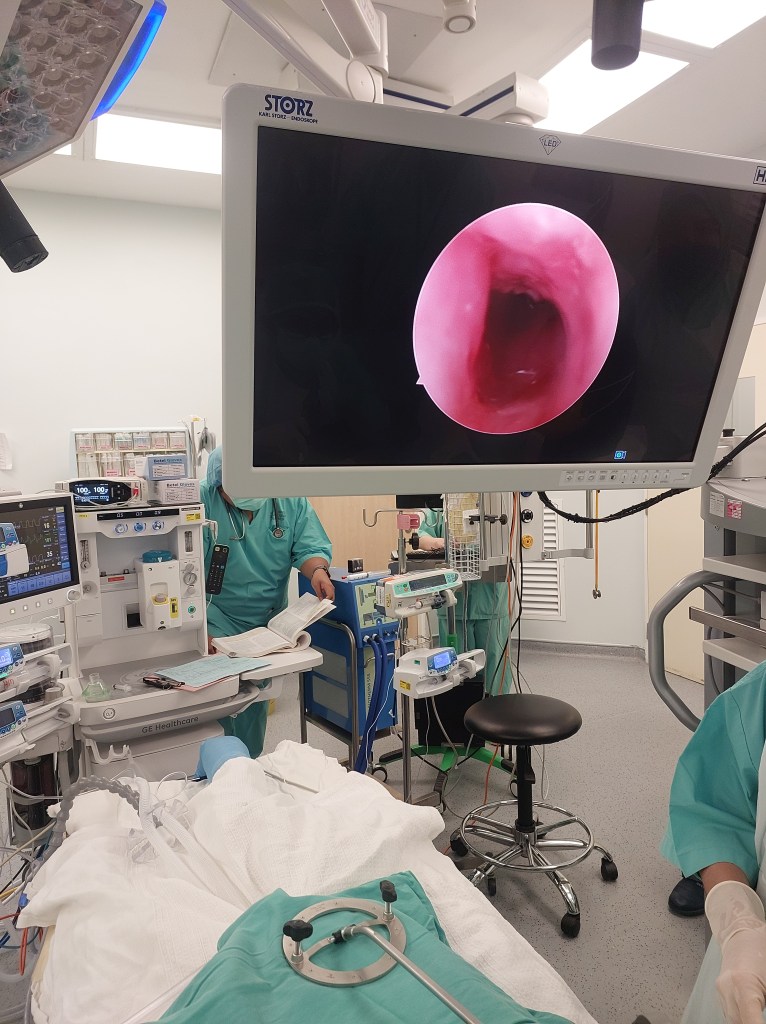
Today, I will discuss a case involving a patient with grade 3 subglottic stenosis. This individual has a medical history that includes hemolymphatic malformation in the anterior chest wall and a mediastinal mass. Furthermore, previous attempts at extubation have been unsuccessful, resulting in the need for a tracheostomy, and multiple dilatation procedures have been performed to manage the subglottic stenosis.
Now, let’s delve into the details of the procedure:


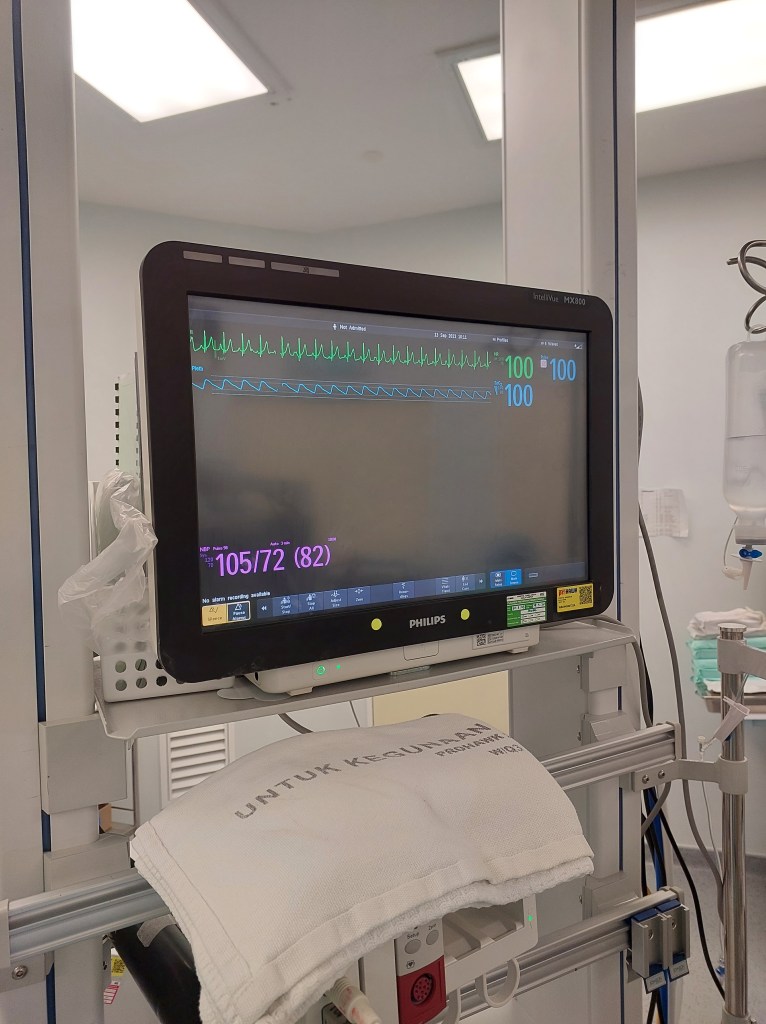































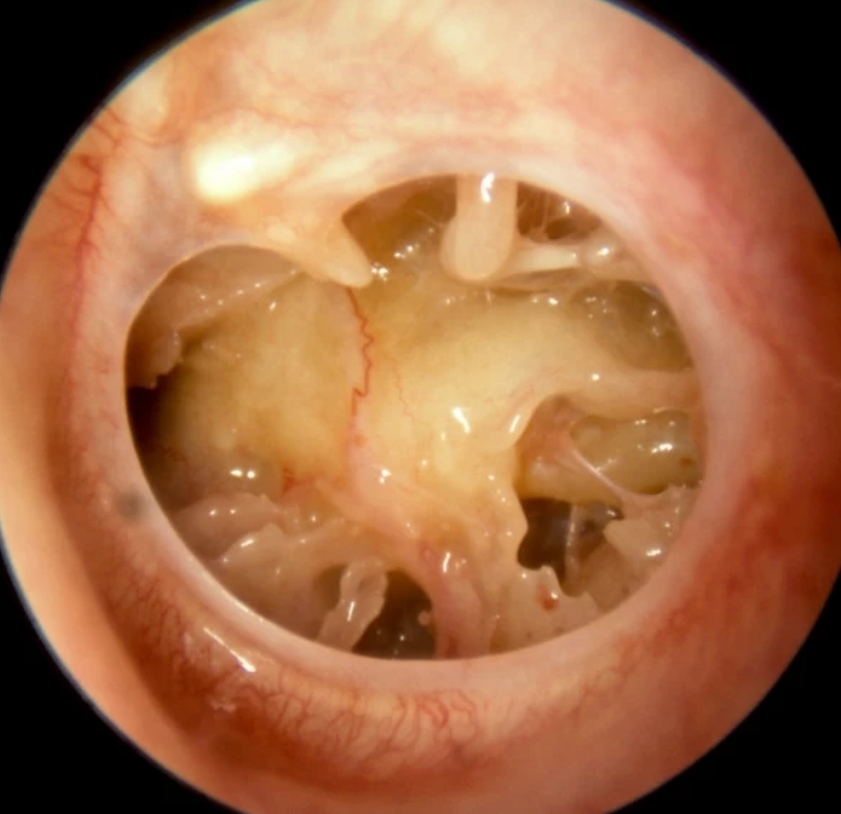

Leave a comment