
Introduction
Music has the incredible power to move our souls, uplift our spirits, and create an immersive experience. However, the excessive exposure to loud music can have detrimental effects on our auditory system. In this article, we will explore the ear-splitting symphony and delve into the various ways in which loud music can damage your ears. So, plug in and prepare to learn about the importance of protecting your hearing in this cacophony of sound.
The Mechanics of Hearing
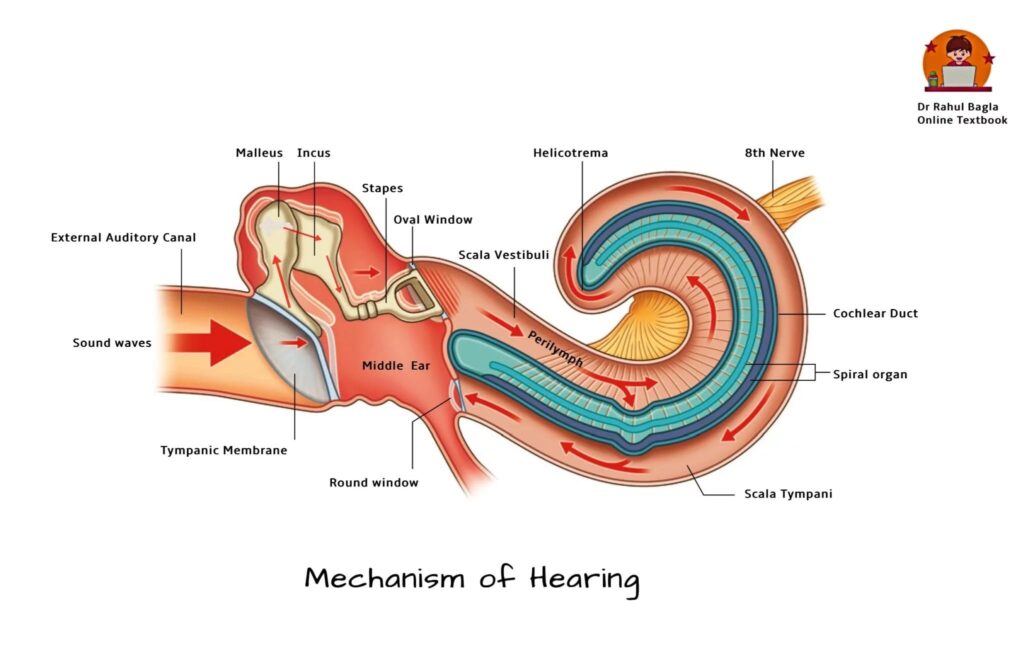
To understand how loud music affects your ears, it’s essential to grasp the mechanics of hearing. The auditory system is a complex network of delicate structures, including the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. When sound waves enter the ear, they travel through the ear canal and vibrate the eardrum, which in turn sets the tiny bones of the middle ear into motion. These vibrations are then transmitted to the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure in the inner ear, where they are converted into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound.
Understanding Decibels: The Measure of Sound
The measurement of sound intensity is quantified using the unit decibels (dB). While soft whispers may range around 30 dB, normal conversation typically registers at approximately 60 dB. As the volume increases, so does the potential damage to your hearing. Exposure to sounds above 85 dB for an extended period can lead to irreversible damage.

The Threshold of Safe Listening
Experts recommend adhering to the 60/60 rule to protect your ears. This rule suggests listening to music at 60% of the maximum volume for no more than 60 minutes per day. By adhering to this guideline, you can enjoy your favorite tunes without putting your hearing at risk.

Prolonged Exposure: A Silent Threat
The danger lies in the cumulative effect of prolonged exposure to loud music. Attending concerts, music festivals, or even using headphones at high volumes for extended periods can gradually damage your hearing. The effects may not be immediately noticeable, but over time, they can lead to permanent hearing loss.

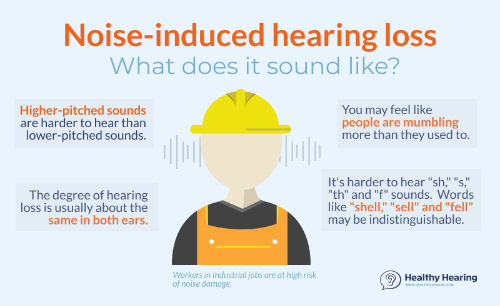
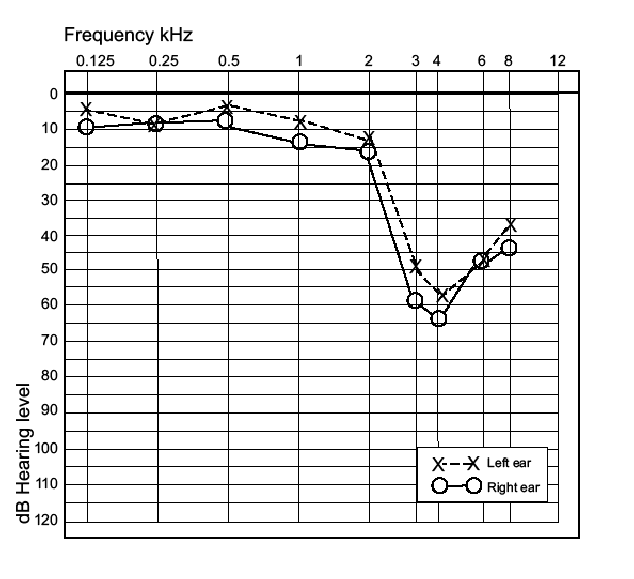
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL)
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL) is a common consequence of exposure to loud music. This type of hearing loss occurs due to damage to the hair cells in the inner ear, which are responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals. Once these hair cells are damaged or destroyed, they cannot regenerate, leading to permanent hearing loss.
Tinnitus: The Unwanted Symphony
Tinnitus, characterized by a persistent ringing or buzzing sound in the ears, is another prevalent side effect of loud music exposure. It can be an incredibly distressing condition, impacting one’s quality of life and causing sleep disturbances and difficulty concentrating.

Temporary Threshold Shift (TTS)
Temporary Threshold Shift (TTS) refers to a temporary decrease in hearing sensitivity following exposure to loud sounds. After attending a loud concert or using headphones at high volumes, you may experience muffled hearing or a sensation of fullness in your ears. While TTS is usually reversible, it serves as a warning sign that your ears have been exposed to potentially damaging noise levels.

Earbuds and Headphones: A Deceptive Convenience
The convenience and portability of earbuds and headphones have made them ubiquitous accessories in our daily lives. However, their improper and excessive use can pose a significant threat to our hearing health. When used at high volumes or for extended durations, these devices deliver intense sound directly into the ear canal, increasing the risk of hearing damage.

Prevention is Key: Protecting Your Ears
Protecting your ears from the damaging effects of loud music is crucial for maintaining healthy hearing. Here are some practical steps you can take to safeguard your auditory health:
1. Use volume-limiting features: Many audio devices and smartphones offer built-in volume controls or limiting features. Take advantage of these settings to cap the maximum volume output.
2. Take listening breaks: Give your ears regular breaks from prolonged exposure to loud music. Create quiet periods in your day to allow your auditory system to recover.
3. Maintain a safe distance: When attending concerts or music events, try to position yourself at a safe distance from the speakers to minimize the impact of loud sound waves on your ears.

Volume Control: A Responsible Approach
Being mindful of the volume level while listening to music is essential. Opt for a comfortable volume that allows you to enjoy the music without straining to hear it. If others can hear the sound leaking from your earphones or headphones, it’s a sign that the volume is too high and potentially damaging.
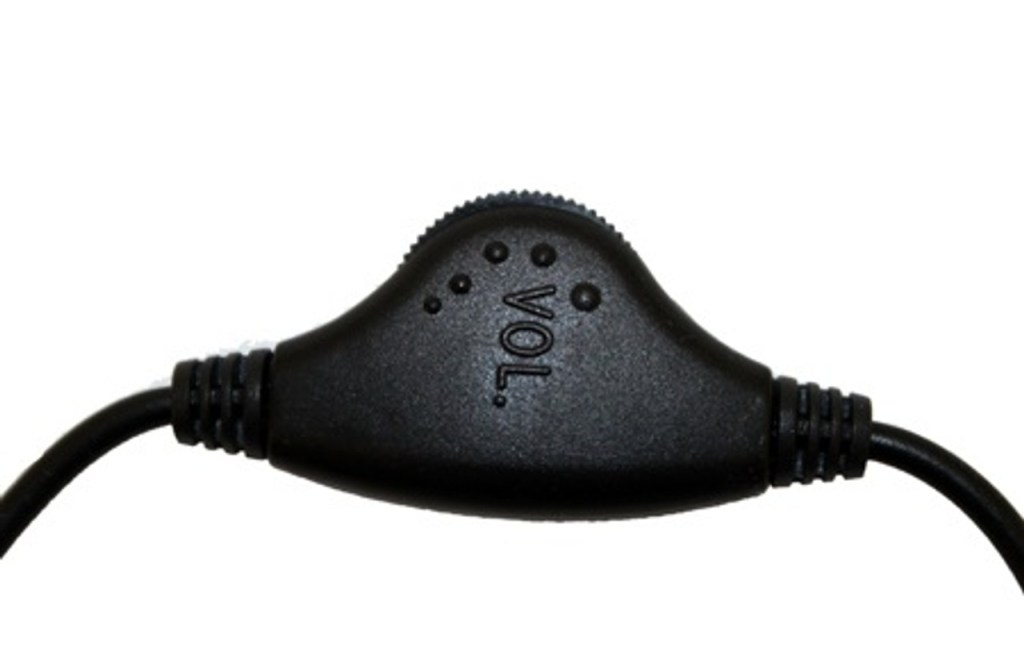

The Role of Earplugs
Earplugs are a practical and accessible solution for protecting your ears in noisy environments. They come in various shapes and sizes and can effectively reduce the intensity of sound without compromising your listening experience. Investing in a high-quality pair of musician’s earplugs can provide excellent protection while maintaining sound fidelity.

Hearing Protection in Music Venues
Music venues often expose concertgoers to high decibel levels. If you frequently attend live performances, consider investing in specialized earplugs designed for musicians and concert enthusiasts. These earplugs are designed to reduce the volume of sound while preserving the clarity and quality of the music.

How Musicians Can Protect Their Hearing
Musicians, who are regularly exposed to amplified sound, face an increased risk of hearing damage. To safeguard their hearing, musicians can adopt the following practices:
- Use in-ear monitors: In-ear monitors provide musicians with a personalized mix of sound while reducing the need for excessive stage volume.
- Take regular breaks: Musicians should take regular breaks during rehearsals and performances to give their ears time to recover from the noise exposure.
- Consult an audiologist: Regular hearing check-ups and consultations with an audiologist can help musicians monitor their hearing health and detect any early signs of damage.
The Psychological Impact of Hearing Loss
Beyond the physical implications, hearing loss can also have a profound psychological impact on individuals. It can lead to feelings of isolation, frustration, and anxiety, as communication becomes challenging. Seeking support from loved ones, hearing loss support groups, and professional counselors can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of hearing loss.

Conclusion
In this ear-splitting symphony, it is crucial to recognize the potential damaging effects of loud music on our ears. By understanding the mechanics of hearing, the concept of decibels, and the risks associated with prolonged exposure, we can take proactive measures to protect our auditory health. Remember, prevention is key, and responsible listening habits, along with the use of hearing protection, can help preserve the beauty of music while safeguarding your ears for years to come.






























Leave a comment