Have you ever felt like you can hear your own voice echoing inside your head when you talk, or even hear your own breathing loudly in your ear? This strange and uncomfortable condition may be due to something called Patulous Eustachian Tube.
Normally, the Eustachian tube (a small canal connecting the back of the nose to the middle ear) stays closed most of the time, and only opens when we swallow, yawn, or chew. This mechanism helps equalize pressure in the ear and keeps things comfortable.
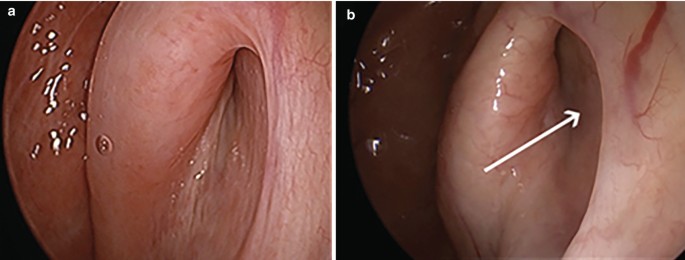
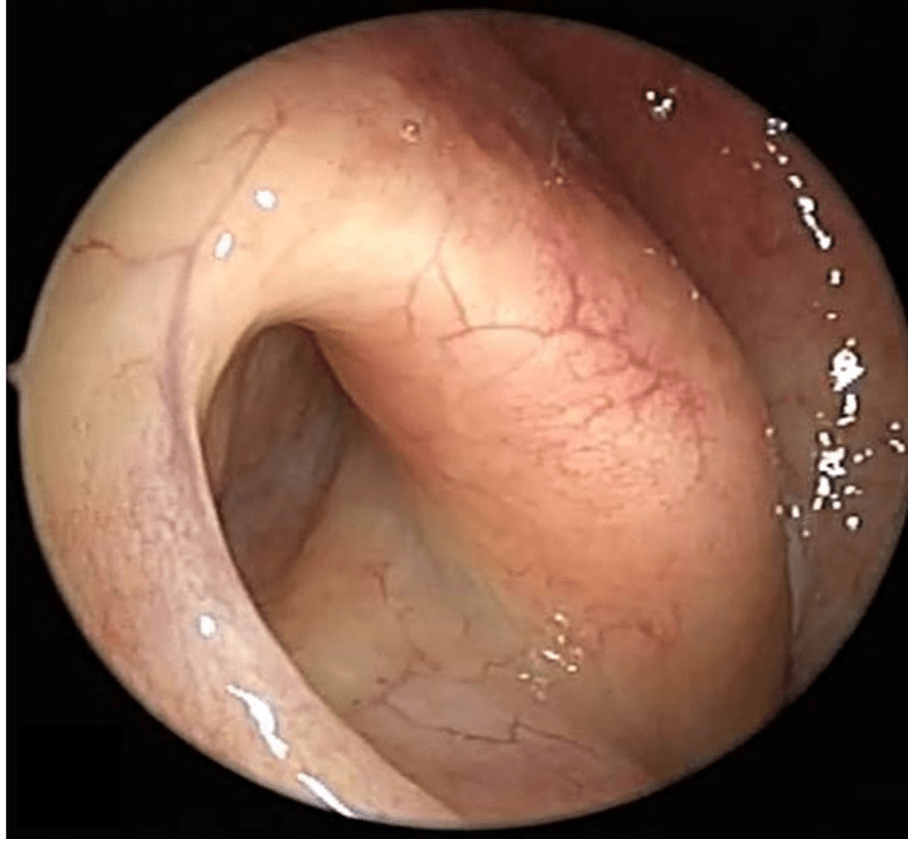
In Patulous Eustachian Tube (PET), the tube stays abnormally open, causing distressing symptoms.
Common Symptoms
People with Patulous Eustachian Tube may experience:
- Autophony – hearing your own voice too loudly in your ear
- Echo-like sensation when speaking
- Hearing your own breathing inside the ear
- A sense of ear “fullness” or blockage, even though the ear canal is clear
- Symptoms that get worse with exercise, stress, or weight loss (because of reduced fat around the tube)
- Symptoms that improve when lying down (as blood flow temporarily narrows the tube)
These symptoms can be very disturbing and often mistaken for sinus, hearing, or balance problems.
How Do We Diagnose It?
An ENT specialist can confirm the condition with several tools:
- History & examination – listening to your symptoms is the most important clue
- Otoscopy – sometimes the ear drum can be seen moving with each breath
- Tympanometry – a special test showing ear drum movements during breathing
- Endoscopy of the nose – to directly assess the Eustachian tube opening
- Hearing tests (audiometry) – to rule out other ear disorders
Because the symptoms may mimic other conditions, it is essential to be assessed by an ENT doctor for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on how severe and persistent the symptoms are.
Medical (Non-Surgical) Treatments
- Nasal drops or sprays (sometimes thickening agents) to help narrow the tube
- Hydration & lifestyle changes – drinking enough water and avoiding rapid weight loss
- Positioning advice – lying down or bending forward can provide temporary relief
- Medications – certain nasal treatments may reduce the abnormal openness of the tube
Surgical Treatments
If medical measures don’t give enough relief, surgical procedures may be considered, such as:
- Injection treatments around the Eustachian tube opening to narrow it
- Cartilage or fat grafting to bulk up and close the tube more effectively
- Other minimally invasive techniques tailored to the patient’s needs
Surgery is usually reserved for severe cases but can significantly improve quality of life.
Why You Shouldn’t Ignore It
Patulous Eustachian Tube is not dangerous, but it can be very frustrating and affect your daily comfort, concentration, and confidence. Many patients struggle with it for years, not knowing what’s wrong.
If you notice these symptoms, especially if they are persistent or worsening, it’s best to see an ENT specialist who can guide you through proper diagnosis and treatment.

Untuk tempah slot appointment klinik dengan saya, sila klik sini (Sunway Velocity Medical Centre) atau sini (Columbia Setapak).
Untuk maklumat lanjut, sila lawati laman web saya di drameenent.com untuk sumber dan perundingan.




























Leave a comment