PART 6: Treatment and Management Options for Neck Swelling
Once the cause of neck swelling is identified, the next question is clear.
👉 “Doctor, how is this treated?”
Treatment for neck swelling is cause-based.
There is no single solution.
Therefore, management must be personalised.
As an ENT specialist, my role is to choose the safest and most effective approach for each patient.
1. Observation and Monitoring
Not all neck swellings require immediate treatment.
Some conditions improve on their own.
These include:
- Reactive lymph nodes after infection
- Mild viral illnesses
- Small benign cysts
In such cases, careful monitoring is advised.
This may involve:
- Regular follow-up visits
- Repeat examinations
- Interval imaging if needed
However, monitoring is never passive.
Changes are tracked closely.

2. Medical Treatment
Medical therapy is often the first step.
Antibiotics
Used when bacterial infection is suspected.
Examples include:
- Acute tonsillitis with lymph node enlargement
- Dental-related infections
- Infected salivary glands
Antibiotics are prescribed only when indicated.
Unnecessary use is avoided.
Anti-inflammatory Treatment
Painful swelling may benefit from:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Pain relief
- Supportive care
This improves comfort while the condition resolves.
Thyroid and Hormonal Management
Thyroid-related neck swelling may require:
- Hormonal treatment
- Endocrinology referral
- Ongoing monitoring
ENT specialists often coordinate care.
3. Treatment of Salivary Gland Conditions
Salivary gland swelling needs targeted management.
Options include:
- Hydration and massage
- Treatment of infection
- Removal of salivary stones
- Surgical intervention in selected cases
The approach depends on cause and severity.
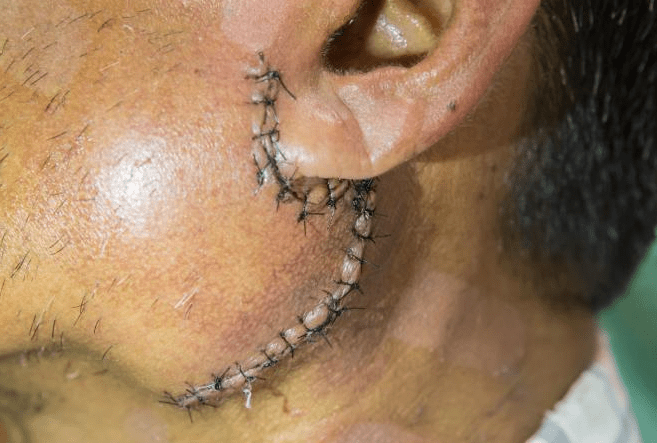
4. Surgical Management
Surgery is considered when:
- The swelling does not resolve
- There is airway or swallowing risk
- Cancer is suspected or confirmed
- The mass causes functional problems
Common surgical procedures include:
- Excision of cysts
- Removal of benign tumours
- Thyroid surgery
- Neck dissection for cancer
Importantly, surgery is planned carefully.
It is never rushed without clear indication.
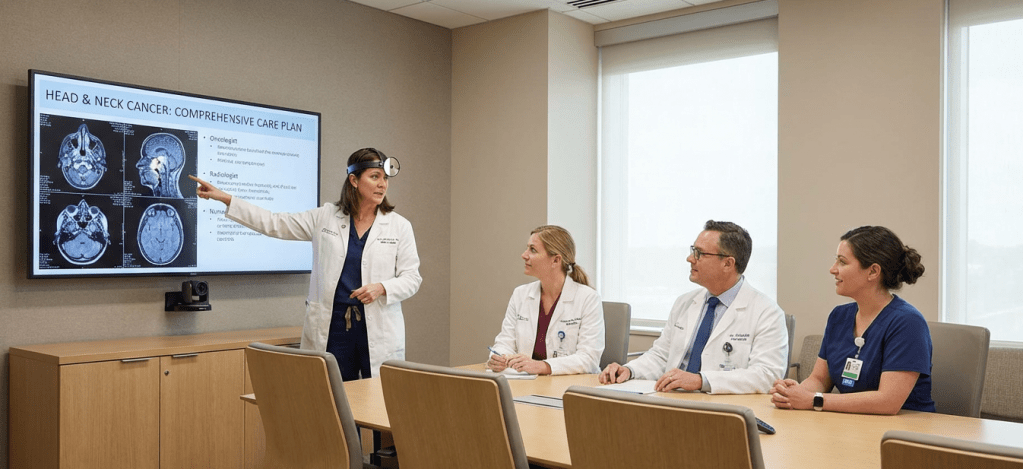

5. Cancer-Related Treatment
When neck swelling is due to cancer, treatment becomes multidisciplinary.
Management may involve:
- Surgery
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Combined treatment approaches
ENT surgeons often lead care alongside:
- Oncologists
- Radiologists
- Pathologists
- Speech and swallowing therapists
Early-stage disease has better outcomes.
This is why early diagnosis matters.
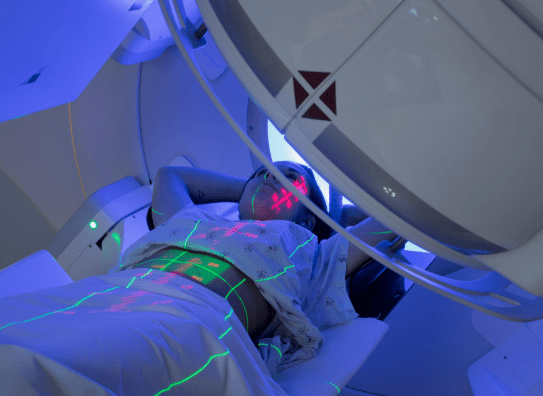
6. Supportive and Rehabilitative Care
Treatment does not stop after therapy.
Supportive care includes:
- Pain management
- Swallowing rehabilitation
- Voice therapy
- Nutritional support
Quality of life is prioritised.
Patients are supported throughout recovery.

7. What Patients Often Worry About
“Will treatment leave scars?”
Modern techniques minimise scarring.
“Will I lose my voice?”
Voice preservation is a key priority.
“Is surgery always needed?”
No. Many neck swellings are treated without surgery.
Clear communication helps reduce fear.
Why Individualised Treatment Matters
Every neck swelling is different.
Treating all lumps the same causes problems.
An ENT-led approach ensures:
- Correct diagnosis
- Appropriate treatment
- Avoidance of overtreatment
- Better long-term outcomes
This approach is backed by ENT clinical evidence.
👉 If you have been diagnosed with neck swelling or are unsure about treatment options, a personalised ENT consultation in Kuala Lumpur ensures safe and appropriate management. Book an appointment to discuss the best treatment plan for your condition.
References
This article is written based on current evidence and clinical practice standards from leading ENT journals, including The Laryngoscope, JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery, Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, Head & Neck, Clinical Otolaryngology, and European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.
Reviewed by Dr Ameen, ENT Specialist, Kuala Lumpur
































Leave a comment