Causes, Symptoms & ENT Treatment in Kuala Lumpur
Ear discharge, medically called otorrhea, is a common ENT symptom that can affect both children and adults, though this page focuses on adult presentation. Discharge from the ear can range from clear fluid to pus or blood, often accompanied by pain, hearing loss, or odor.
While some cases are minor, persistent or recurrent ear discharge can indicate infection, chronic ear disease, or rarely, more serious conditions. Timely evaluation by an ENT specialist is essential to prevent complications.
What Does Ear Discharge Feel Like?
Patients may notice:
- Fluid or pus draining from the ear
- Wet or crusted ear canal
- Ear fullness or pressure
- Itching or irritation in the ear
- Hearing difficulty
- Foul smell (in infection)
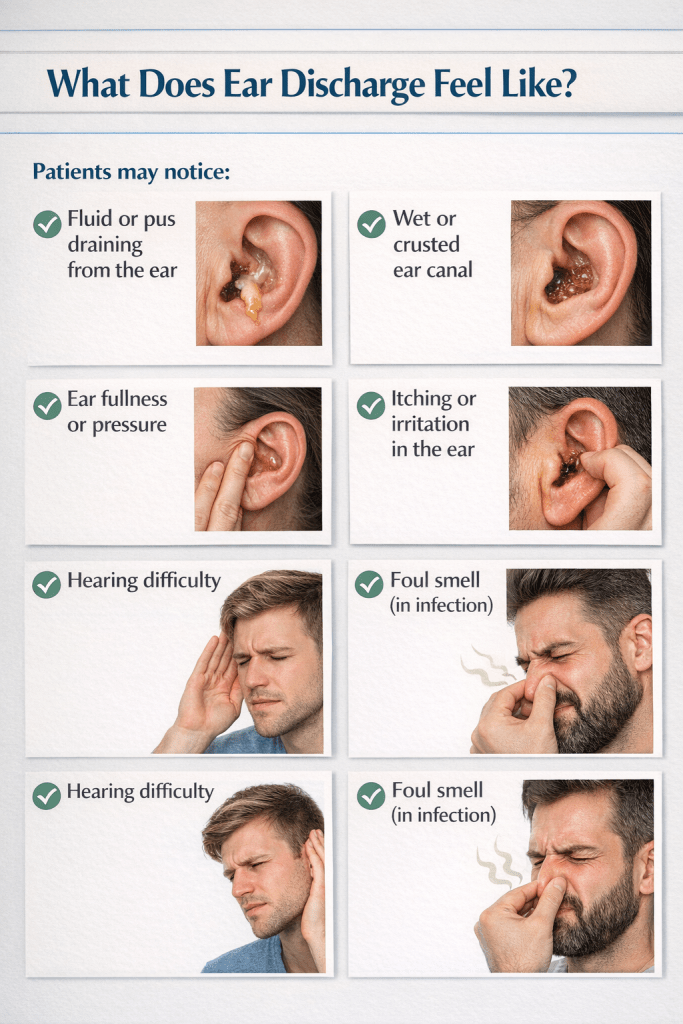
Common Causes of Ear Discharge
1. Acute Otitis Media with Perforation
Middle ear infection can rupture the eardrum, causing pus or fluid to drain.
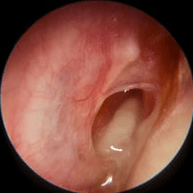
2. Chronic Otitis Media
Long-standing ear infections often produce persistent discharge, sometimes with hearing loss.
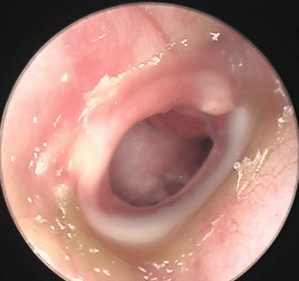
3. Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear)
Outer ear infection from moisture or trauma can lead to discharge, pain, and redness.
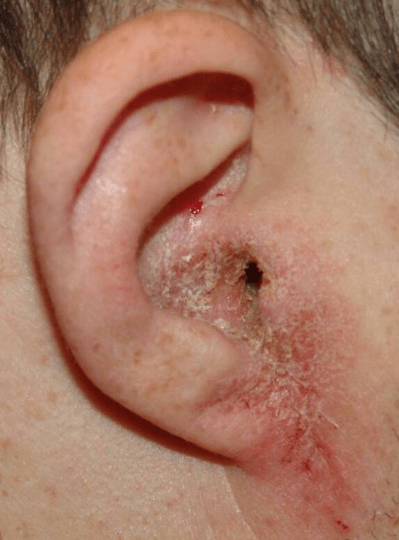
4. Foreign Bodies
Objects in the ear canal may irritate tissue, causing discharge or infection.
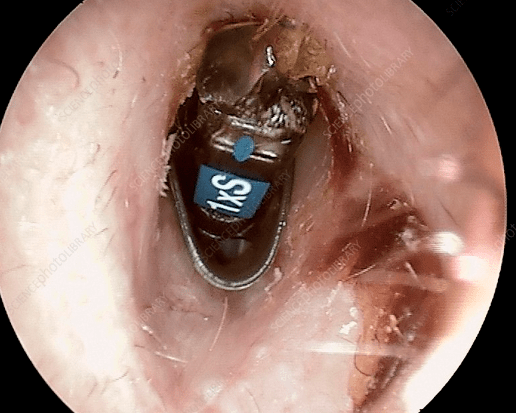
5. Trauma or Ear Surgery
Post-surgical drainage or injury can result in temporary ear fluid.
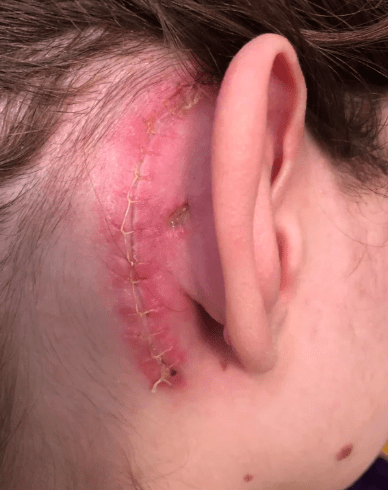
6. Rare Causes
Cholesteatoma or tumors may cause foul-smelling or bloody discharge; early ENT assessment is critical.
🚨 When Should You Worry About Ear Discharge?
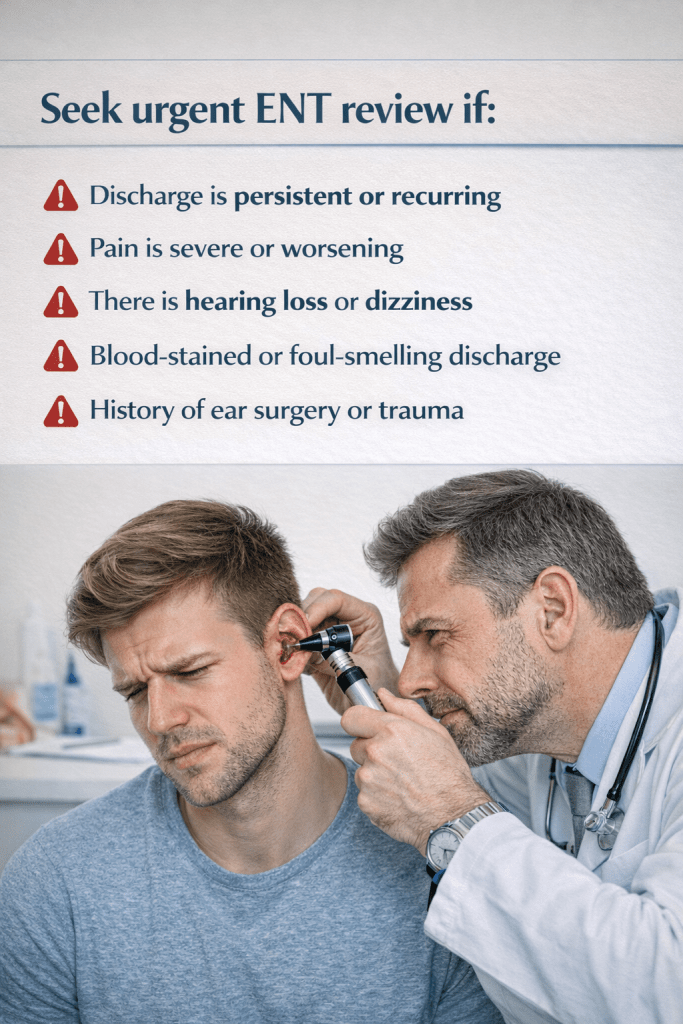
Seek urgent ENT review if:
- Discharge is persistent or recurring
- Pain is severe or worsening
- There is hearing loss or dizziness
- Blood-stained or foul-smelling discharge
- History of ear surgery or trauma
How an ENT Specialist Evaluates Ear Discharge
ENT assessment includes:
- Detailed history of onset, duration, and type of discharge
- Ear examination using otoscope or microscope
- Hearing tests if required
- Endoscopic evaluation for chronic or recurrent cases
- Imaging if structural abnormality is suspected
Treatment Options for Ear Discharge
✅ Medical Treatment
- Antibiotics (oral or ear drops) for bacterial infections
- Ear cleaning under professional supervision
- Pain relief and anti-inflammatory medication
✅ Surgical or Procedural Treatment
- Myringotomy or tympanostomy tubes for chronic middle ear disease
- Removal of cholesteatoma or growths if detected
- Repair of eardrum perforation when indicated
Treatment is tailored to cause, severity, and duration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can ear discharge go away without treatment?
Mild outer ear discharge may resolve, but persistent or middle ear discharge requires ENT care.
Q: Should I put drops in the ear myself?
Only under guidance. Improper use can worsen infection or damage the ear.
Q: Can chronic discharge cause hearing loss?
Yes. Untreated infections can damage the eardrum or middle ear bones.
When Should You See an ENT Specialist in Kuala Lumpur?
Consult an ENT specialist if:
- Ear discharge lasts more than a few days
- You notice foul smell, blood, or hearing loss
- Symptoms recur frequently
Proper ENT assessment ensures accurate diagnosis and prevents complications such as chronic infection or permanent hearing loss.
👨⚕️ ENT Specialist’s Perspective
Ear discharge is a symptom, not a diagnosis. From an ENT perspective, persistent otorrhea requires thorough examination to distinguish between outer ear, middle ear, and rare serious causes. Early specialist intervention preserves hearing and prevents complications.
Reviewed by Dr Ameen, ENT Specialist, Kuala Lumpur