Causes, COVID, Sinus & When to See an ENT Specialist
Loss of smell, medically known as anosmia, is a symptom that many people only notice when it is gone. Smell plays a vital role in taste, safety, appetite, and quality of life. When it becomes reduced or absent, it may indicate an underlying nasal, sinus, or neurological condition.
As an ENT specialist, I commonly see patients who delayed seeking medical advice, assuming their sense of smell would return on its own.
What Is Loss of Smell?
Loss of smell can be:
- Partial (hyposmia)
- Complete (anosmia)
- Sudden or gradual
It may affect one or both nostrils and can significantly reduce enjoyment of food and detect hazards such as smoke or gas.
Common Causes of Loss of Smell
1. Nasal and Sinus Inflammation
The most common cause.
Includes:
- Allergic rhinitis
- Acute or chronic sinusitis
- Nasal polyps
Inflammation blocks odour molecules from reaching the smell receptors.
2. Post-Viral Infection (Including COVID-19)
Viral infections can temporarily or permanently damage the smell nerve.
Features:
- Sudden loss of smell
- Often without severe nasal blockage
- May take weeks or months to recover
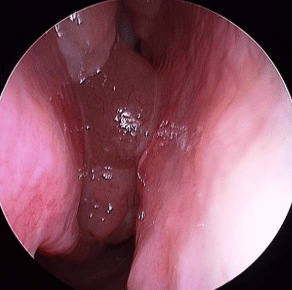
3. Nasal Polyps
Soft growths inside the nasal cavity interfere with airflow and smell perception.
4. Head Injury
Trauma may damage the olfactory nerve.
5. Age-Related Smell Loss
Gradual reduction of smell sensitivity with ageing.
6. Neurological Conditions (Rare)
Such as Parkinson’s disease or brain tumours.
🚨 When Should You Worry About Loss of Smell?
Seek ENT assessment if:
- Smell loss lasts more than 2–3 weeks
- It is not improving after flu or COVID
- It is associated with persistent nasal blockage
- There is one-sided nasal obstruction
- There is history of head injury
Early evaluation improves the chance of recovery.
How an ENT Specialist Evaluates Loss of Smell
Assessment includes:
- Detailed history of onset and progression
- Nasal examination
- Nasal endoscopy to detect polyps or inflammation
- Imaging (CT or MRI) if indicated
This allows accurate identification of reversible causes.
Treatment Options for Loss of Smell
✅ Medical Treatment
- Intranasal steroid sprays
- Short courses of oral medication when indicated
- Saline nasal irrigation
✅ Smell Training
A structured smell training programme may help recovery, especially after viral infections.
✅ Surgical Treatment
- Removal of nasal polyps
- Endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic sinus disease
Treatment depends on the underlying cause, not just the symptom.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Will my sense of smell return?
Many cases improve, especially if treated early.
Q: Can COVID-related smell loss be permanent?
Most recover, but some require long-term management.
Q: Does blocked nose always cause loss of smell?
Not always, but nasal obstruction is a common contributor.
When Should You See an ENT Specialist in Kuala Lumpur?
You should consider ENT consultation if:
- Loss of smell affects daily life or safety
- Symptoms persist beyond a few weeks
- Over-the-counter treatments fail
- You have sinus or nasal symptoms
ENT evaluation improves diagnosis and recovery outcomes.
Reviewed by Dr Ameen, ENT Specialist, Kuala Lumpur