
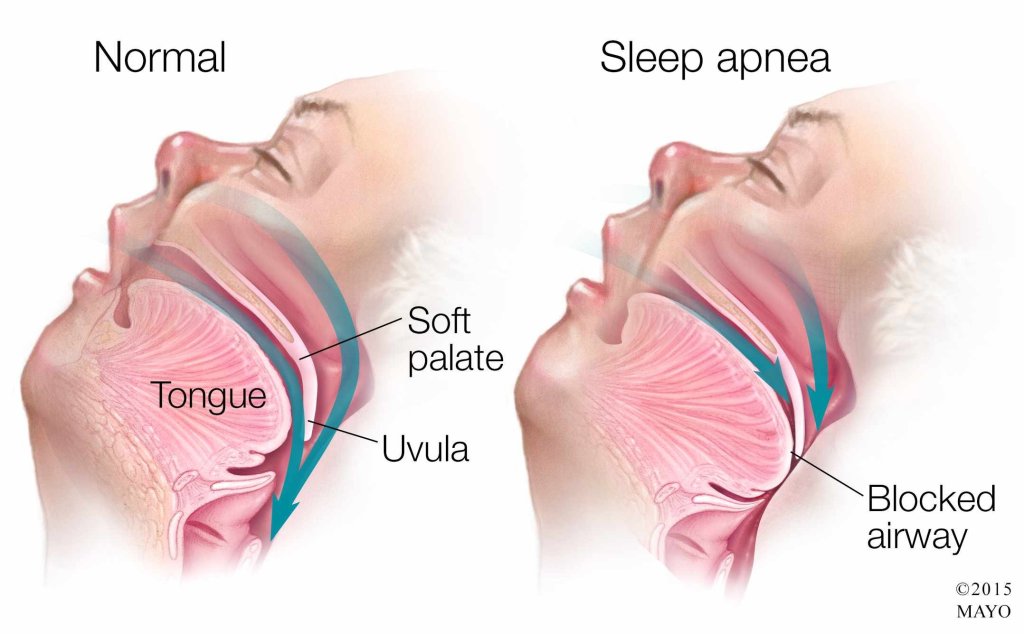
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common sleep disorder that affects all age groups and is associated with many co-morbid diseases (especially cardiovascular diseases). Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is the gold standard for treating OSA. However, adherence to PAP therapy has been a major challenge with an estimated adherence between 20% and 80%.
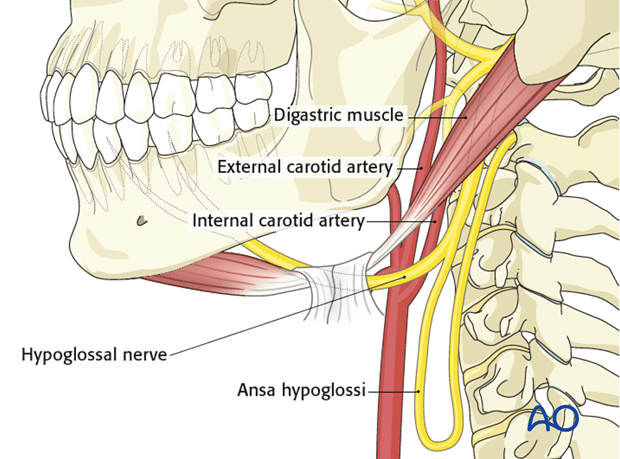
Obstructive sleep apnea is characterized by repetitive upper airway collapse during sleep. Upper airway patency is maintained by contraction of the upper airway dilator muscles. There are several upper airway dilator muscles. The most important upper airway dilator muscle is the genioglossus muscle which has phasic activity during inspiration. The genioglossus muscle is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII).
Upper airway stimulation (UAS) is a more recent surgical option for treating obstructive sleep apnea with a success rate of about 75% at 5 years
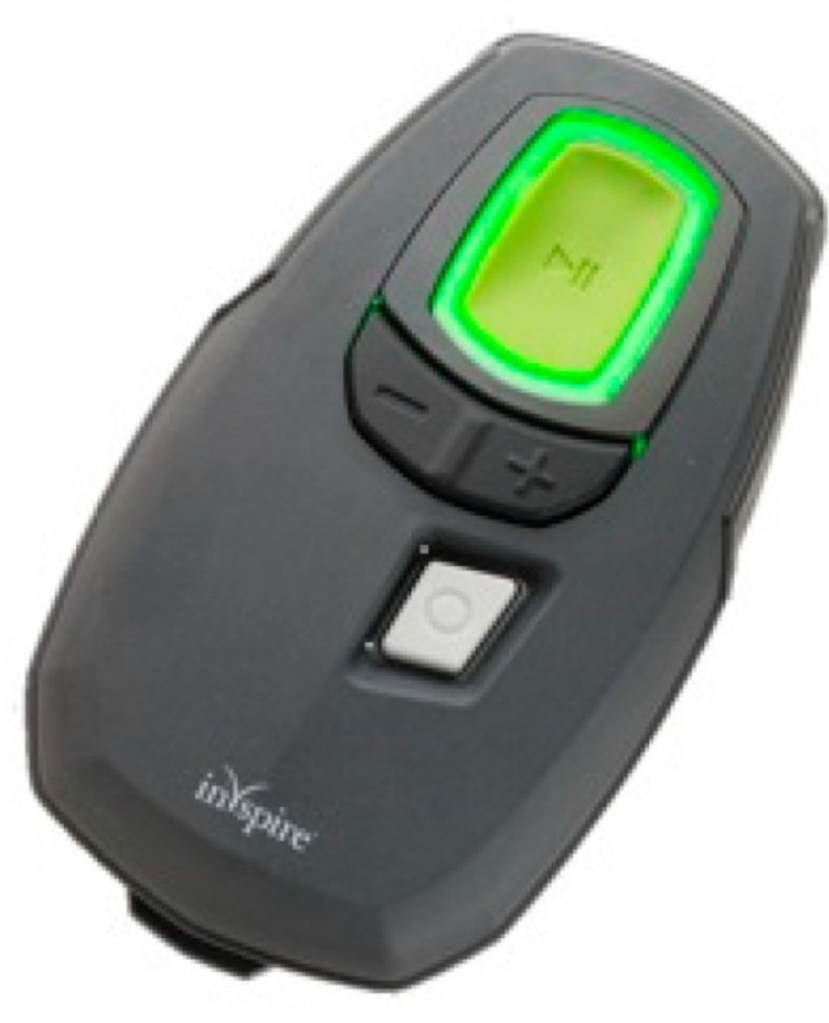


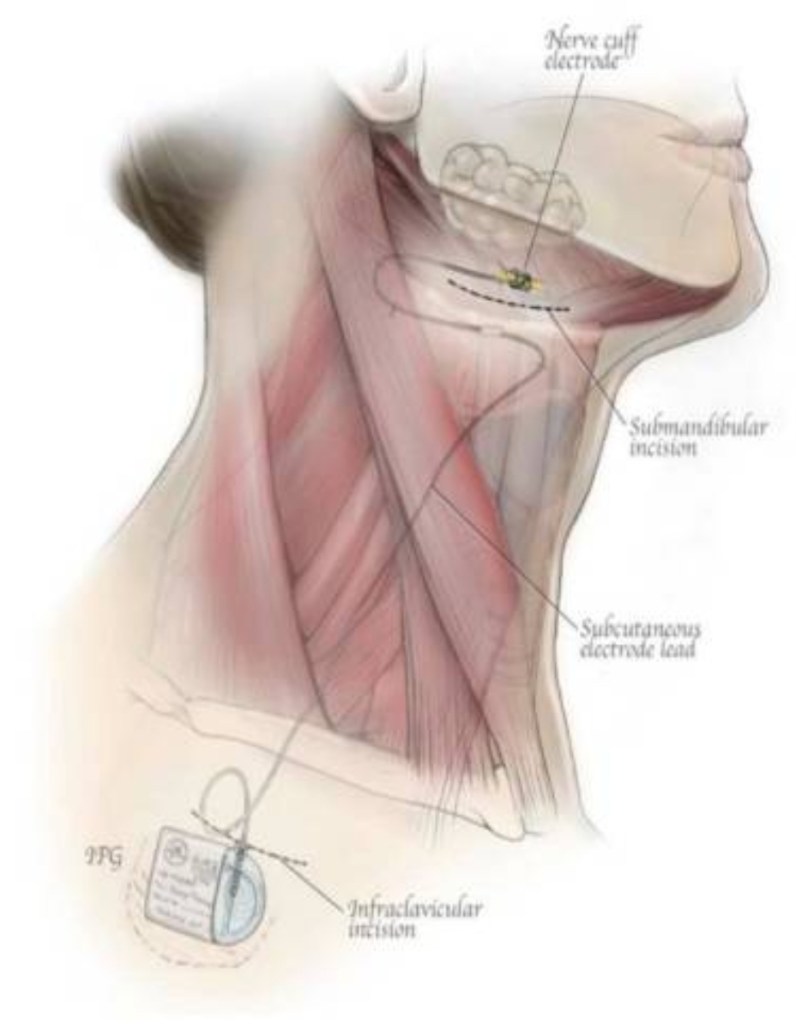
Introducing a device approved by the FDA, Inspire Medical Systems (Maple Grove, MN, USA). It is a hypoglossal nerve stimulator that generates electrical impulses through a generator that is implanted in the upper right chest (under the skin). The impulse is transmitted via a tunneled lead that ends up with a cuff that surrounds the hypoglossal nerve.
INDICATION
UAS is indicated in patients with moderate and severe OSA (AHI greater more or equal to 15 events per hour and less than or equal to 65 events per hour) who cannot tolerate or failed positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy.
CONTRAINDICATION
UAS is contraindicated in patients with central sleep apnea (defined as a central apnea–hypopnea index of more than 25% of the total AHI), and in patients with sleep-related hypoxia or hypoventilation (such as patients with severe obstructive or restrictive pulmonary diseases). One of the factors that has been shown to be significantly correlated with the success of UAS is body mass index (BMI). BMI ≥ 32 kg/m2 is less likely to be associated with a successful outcome from UAS.
PRE-OP EVALUATION
Evaluation of the upper airway endoscopically is performed utilizing Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy (DISE), specifically looking for anteroposterior tongue base and palate collapse. Patients with complete concentric collapse at the level of the velum are poor candidates.
FOLLOW UP
Six weeks after implantation, the patient visits with a sleep provider to activate the generator (this process was discussed earlier in this review). Two months later, a full-night lab titration study is conducted to ensure the effectiveness of the Inspire settings (mainly functional threshold) in all sleep stages and in all sleep positions. Then, follow up visits at 3, 6, and 12 months can be scheduled to evaluate the long-term clinical outcome.

KOMEN SAYA
Untuk pesakit berdengkur Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), penggunaan CPAP machine dikatakan GOLD STANDARD oleh pakar kesihatan pernafasan. Tetapi, CPAP juga ada kelemahannya yang tersendiri iaitu bising dan topeng yang tidak sesuai atau berkesan (sebab hidung sumbat atau ketidaksesuaian bentuk muka)
Maka UAS/HGNS ni merupakan salah satu pilihan lain untuk menangani masalah tersebut. Pesakit boleh mendapat faedah daripada alat ini sehingga 5 tahun selepas pembedahan 👏👏👏. Saya harap teknologi ini akan berkembang di Malaysia dan dapat menolong lebih banyak pesakit OSA.
Sila layari video di bawah untuk belajar dengan lebih lanjut tentang HGNS dari Inspire medical device ini 😁





























Leave a reply to ameenlfc Cancel reply